Online services
Introduction
This tutorial guides you through the process of configuring access management.
To access TomTom Online Services, ANA needs a JSON Web Token (JWT).
TomTom's Access Management Service (AMS) manages access to TomTom Online Services through these access tokens.
Prerequisites
Before setting up access management, ensure that:
-
You have whitelisted the following Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) to allow communication with TomTom services:
api.tomtom.com.hosteddelivery.tomtom.com(all subdomains ofhosteddelivery.tomtom.com)dcas.tomtom.comdcas-hub-01-westeu-prd.azure-devices.net- the FQDN of the AMS deployment you received from your TomTom representative (see below)
-
You have open access to the following outbound ports:
443– for secure HTTPS communication for REST APIs.8883– for secure MQTT communication.
Choosing an access management approach
Depending on your development phase, you can choose to utilize an evaluation access token or connect your Identity and Access Management (IAM) Service to generate JWT tokens.
The following sections detail both scenarios.
Using evaluation access token
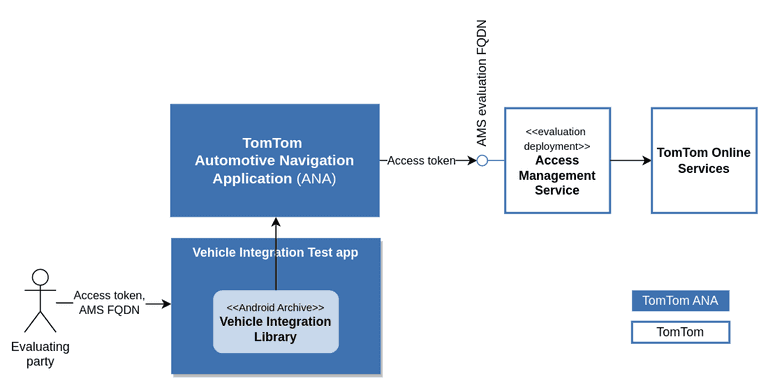
A dedicated evaluation deployment of AMS is available for evaluation purposes.
This deployment allows you to use a predefined evaluation access token.
In case you're evaluating ANA, please contact your TomTom representative to obtain an evaluation access token and the FQDN of the AMS evaluation deployment. Once you have obtained the evaluation access token, you can use the Vehicle Integration Test App to provision the token and AMS FQDN to ANA.
Integrating your Identity and Access Management service
In case you're embedding ANA in your In-Vehicle Infotainment solution, you are required to manage the identity per vehicle or user.
And, once authenticated, issue a JWT token with the required set of claims.
A dedicated deployment of AMS will integrate with your IAM service and use this token to authenticate requests to TomTom Online Services.
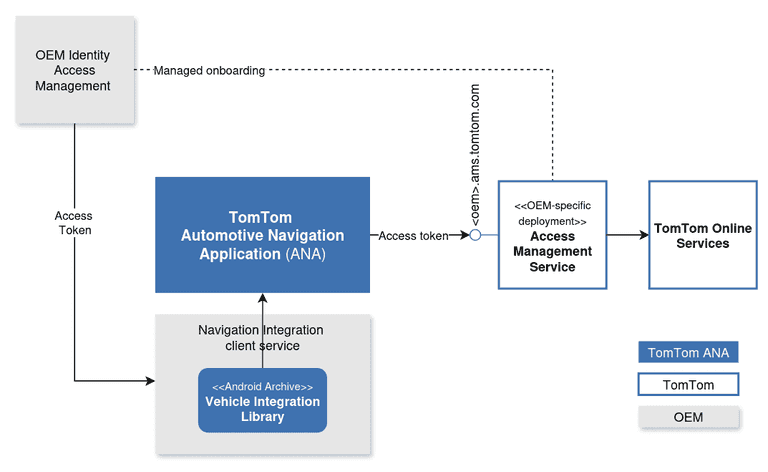
Please contact your TomTom representative to:
- onboard your identity provider to our Access Management Service.
- obtain the FQDN of the dedicated AMS deployment.
- understand the necessary claims in the JWT token to match the requirements of the Automotive Navigation Application.
Provision the access token to ANA
The Vehicle Integration Library (VIL) provides methods to set the access token and AMS FQDN to ANA.
See Vehicle integration basics to learn how to integrate the VIL into your application.
After integrating the VIL, use its OnlineServicesManager to provision the access token and AMS FQDN.
Step 1: Create an OnlineServicesTokenParameters instance
Create an instance of OnlineServicesTokenParameters with your access token:
1import com.tomtom.automotive.integration.vehicle.client.api.onlineServices.authentication.OnlineServicesTokenParameters23val tokenParameters = OnlineServicesTokenParameters(4 authenticationToken = "your.access.token"5)
Step 2: Create an OnlineServicesTokenParameters instance
Create an instance of OnlineServicesConfigurationParameters with the FQDN of the AMS deployment:
1import com.tomtom.automotive.integration.vehicle.client.api.onlineServices.configuration.OnlineServicesConfigurationParameters23val configParameters = OnlineServicesConfigurationParameters(4 onlineServicesFQDN = "your.ams.fqdn"5)
Step 3: Set the access token
Use vilClient to set the access token:
1vilClient.getOnlineServicesManager().setAuthenticationToken(2 tokenParameters,3 object : OnlineServicesCallback {4 override fun onResult(result: Result<VehicleSpecsParameters, VehicleSpecsFailure>) {5 if (result is Result.Failure) {6 if (result.reason == OnlineServicesFailure.FAILED_TO_SET_TOKEN) {7 // Handle token setting failure8 } else {9 // Handle other failures10 }11 } else {12 // access token set successfully13 }14 }15 })
When setting the authentication token, the following errors may occur:
FAILED_TO_SET_TOKEN: The token could not be set. This could be due to various reasons such as network issues or an invalid token format.UNHANDLED: An unexpected error occurred.
Make sure to handle these errors appropriately in your callback implementation.
Step 4: Set the FQDN
Use vilClient to set the FQDN:
1vilClient.getOnlineServicesManager().setOnlineServicesConfiguration(2 configParameters,3 object : OnlineServicesCallback {4 override fun onResult(result: Result<VehicleSpecsParameters, VehicleSpecsFailure>) {5 if (result is Result.Failure) {6 if (result.reason == OnlineServicesFailure.FAILED_TO_SET_CONFIGURATION) {7 // Handle FQDN setting failure8 } else {9 // Handle other failures10 }11 } else {12 // FQDN set successfully13 }14 }15 })
When setting the FQDN, the following errors may occur:
FAILED_TO_SET_CONFIGURATION: The configuration could not be set. This could be due to network issues.INVALID_FQDN_FORMAT: The provided FQDN is not valid.UNHANDLED: An unexpected error occurred.
Make sure to handle these errors appropriately in your callback implementation.
Best practices and considerations
When developing the integration between the Identity Access Management (IAM) Client and the Automotive Navigation Application, consider the following best practices to ensure a smooth and efficient experience:
- Ensure the Vehicle IAM Client can successfully authenticate the Vehicle with your IAM Service to request a valid token. Ideally, this token should be generated at the startup of the device and made readily available to our application.
- Manage token expiration effectively so that the token used in the Automotive Navigation Application remains valid. Implement checks to prevent race conditions during token refreshing, especially when interacting with the IAM Service.
- Ensure that the API operates asynchronously to enhance responsiveness.
By adhering to these key considerations, you can enhance the reliability and efficiency of the integration, ensuring a seamless experience for end-users.