Horizon points of interest (POIs)
A point of interest (POI) is a location that holds particular significance or interest to drivers. Unlike search SDKs, which can provide various types of POIs based on user queries, horizon focuses on delivering POIs along the navigation trajectory, including:
- Rest area
- Gas station
- Electric vehicle charging station
Configuring the horizon engine
Having completed the Retrieving horizon data guide, you are now able to set up the horizon engine and start navigation to retrieve horizon data.
Specifying horizon options
To subscribe to POI elements, create HorizonOptions via the buildHorizonOptions method and specify PoiElementType2 in the list of element types of interest. The horizon path parameters defined within buildHorizonOptions are appropriate for most use cases and can be utilized in both free driving and active guidance scenarios. The buildHorizonOptions method will create a HorizonOptions instance with a main path search distance that is the minimum between 25 km and the remaining route length when navigating with a route, or 10 km when free driving.
val horizonOptions =buildHorizonOptions(listOf(PoiElementType2))
When using the Extended flavor
The Extended flavor of Maps and Navigation SDK for Android is only available upon request. Contact us to get started.
If you prefer to configure the horizon path parameters manually, you can create the HorizonOptions as follows:
1val horizonOptions =2 HorizonOptions(3 elementTypes = listOf(PoiElementType2),4 mainPathSearchOptions =5 MainPathSearchOptions(6 searchDistancePolicy = ExplicitDistancePolicy(7 searchDistance = PathSearchDistance(maxHorizonLength = Distance.kilometers(5)),8 ),9 ),10 subPathSearchOptions = listOf(11 SubPathSearchOptions(12 searchDistance = PathSearchDistance(maxHorizonLength = Distance.meters(100)),13 ),14 ),15 numberOfPaths = 10,16 )
Registering a horizon updated listener
Before starting navigation, register a HorizonUpdatedListener to listen for horizon updates with the horizon options you have defined.
tomTomNavigation.addHorizonUpdatedListener(horizonOptions, horizonUpdatedListener)
Starting navigation
Next, initiate navigation using a route, as outlined in the Retrieving horizon data guide.
1val routePlan = RoutePlan(route, routePlanningOptions)2val navigationOptions = NavigationOptions(routePlan)3tomTomNavigation.start(navigationOptions)
Retrieving POI data
With the navigation started, you can listen for horizon updates and retrieve POI data. Horizon provides the following POI properties. Please refer to the code snippet below to learn how to access them.
- ID
- Name
- Coordinate
- Entry points
- Categories
- Brands
- Opening hours
- Details of charging station (only available if the POI is an electric vehicle charging station)
1private val horizonUpdatedListener = object : HorizonUpdatedListener {2 private var horizonSnapshot: HorizonSnapshot? = null34 override fun onPositionUpdated(5 options: HorizonOptions,6 position: HorizonPosition,7 ) {8 horizonSnapshot?.let { horizonSnapshot ->9 horizonSnapshot.mainPath()10 ?.getElements(PoiElementType2)11 ?.map { it as PoiElement2 }12 ?.forEach { poiElement ->13 Log.v(TAG, "ID: ${poiElement.place.id}")14 Log.v(TAG, "Name: ${poiElement.place.name}")15 Log.v(TAG, "Coordinate: ${poiElement.place.coordinate}")16 Log.v(TAG, "Entry points: ${poiElement.place.entryPoints}")17 Log.v(TAG, "Categories: ${poiElement.place.details?.categoryIds}")18 Log.v(TAG, "Brands: ${poiElement.place.details?.brands}")19 Log.v(TAG, "Opening hours: ${poiElement.place.details?.openingHours}")20 Log.v(TAG, "Charging park: ${poiElement.place.details?.chargingPark}")21 }22 }23 }2425 override fun onHorizonReset(options: HorizonOptions) {26 Log.v(TAG, "Horizon reset")27 }2829 override fun onSnapshotUpdated(30 options: HorizonOptions,31 snapshot: HorizonSnapshot,32 ) {33 horizonSnapshot = snapshot34 }35}
AccessType of a POI
PoiElement2 has an accessType property that indicates whether the POI is accessible from a regular road or a highway exit.
In most cases, highway facility POIs, such as rest areas, are located on service roads that connect to the highway via ramps. If drivers want to access these POIs, they need to take the specific highway exit first. For example, considering a rest area POI as illustrated below:
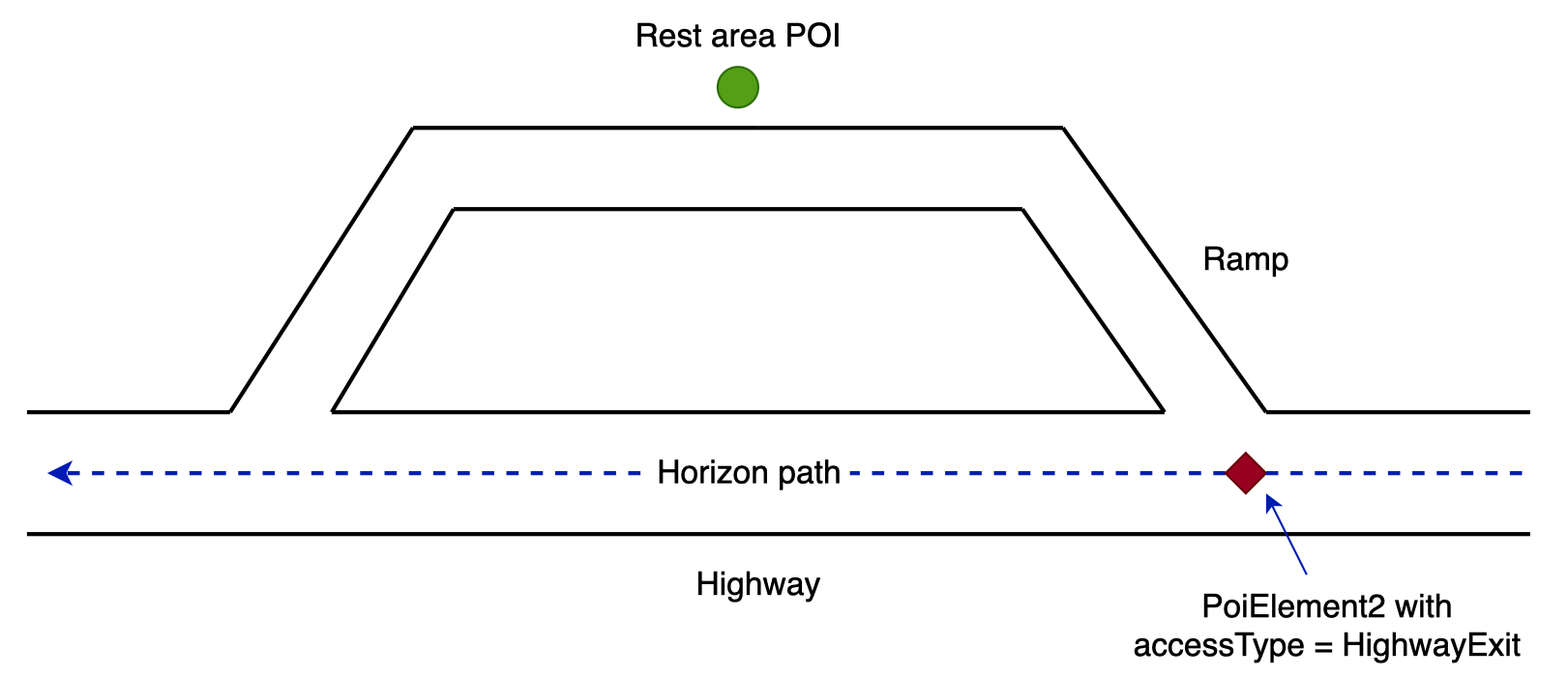
If a horizon path is on the highway and it does not take the highway exit, horizon will deliver one PoiElement2 instance for this POI with the accessType set to AccessType.HighwayExit. This indicates to drivers that the POI can be accessed after taking the highway exit.
However, if a horizon path takes the highway exit and goes through the rest area as illustrated below, horizon will deliver two PoiElement2 instances for this POI, one with the accessType set to AccessType.HighwayExit, and the other one set to AccessType.Regular. The two PoiElement2 instances have the same POI data (PoiElement2.place) but different offsets on the horizon path (PoiElement2.startOffset and PoiElement2.endOffset).
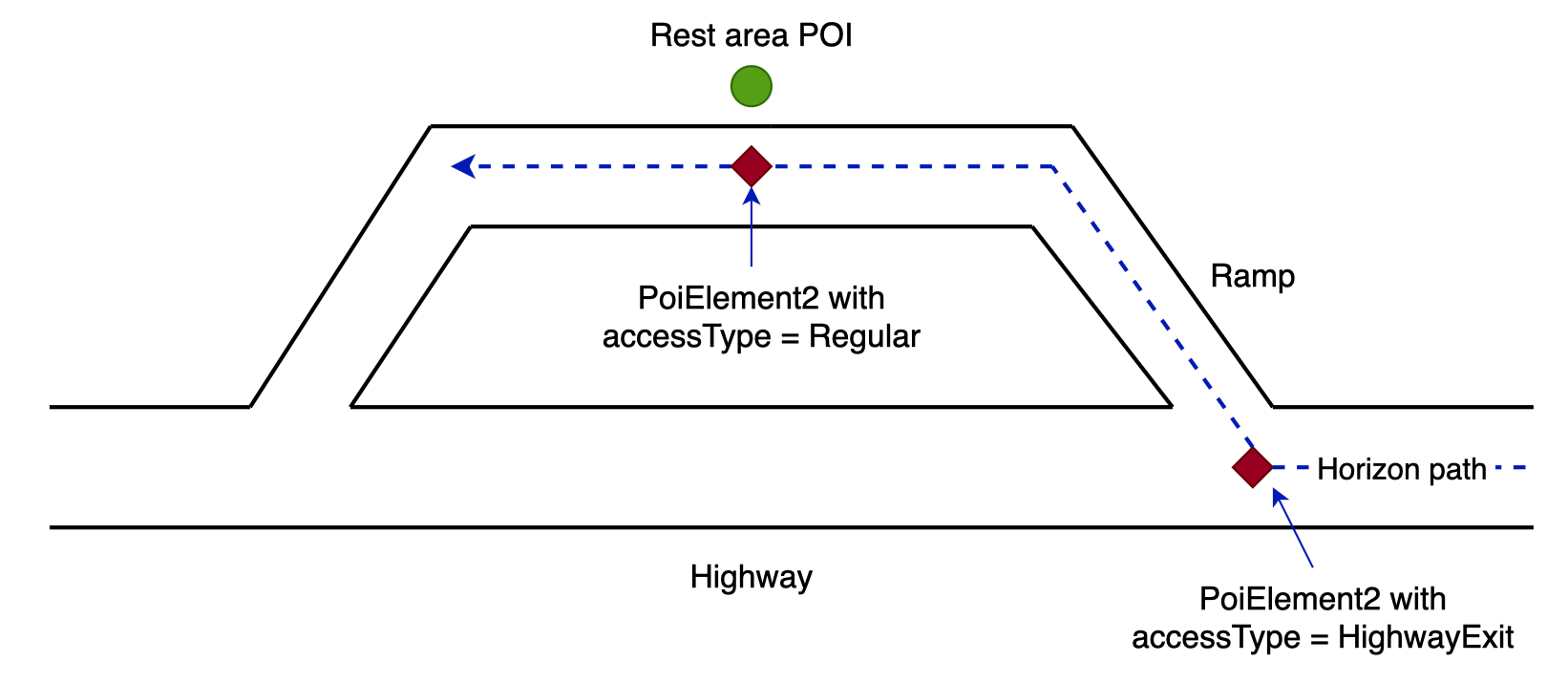
Applications can implement their own logic to determine how to display the two PoiElement2 instances. For example, display both of them and indicate that they are connected, or filter out one of them based on the accessType value.
Next steps
Now that you know how to retrieve horizon POI data, here are the recommendations on what to explore next: