Turn-by-turn navigation
Navigation SDK for Android is only available upon request. Contact Sales to get started.
Turn-by-turn navigation provides real-time guidance along a calculated route. It informs the user about upcoming maneuvers and tracks progress along the route. To get started, add the Navigation module to your project and initialize a TomTomNavigation object. Refer to the Quickstart guide for setup instructions.
Starting navigation
Once the TomTomNavigation object is initialized, you can start navigation. Turn-by-turn navigation requires NavigationOptions , which must include an active RoutePlan.
A RoutePlan consists of a Route and the corresponding RoutePlanningOptions object. To learn how to plan a Route, see the Planning a route guide.
val routePlan = RoutePlan(route = route, routePlanningOptions = routePlanningOptions)
Next, use the prepared RoutePlan to create NavigationOptions, then start navigation by calling the start(NavigationOptions) method on your TomTomNavigation object.
tomTomNavigation.start(NavigationOptions(routePlan))
You can also stop the current navigation session manually using TomTomNavigation.stop(). This clears all related session data:
tomTomNavigation.stop()
If navigation has not been started, calling the stop method has no effect.
Updating the route
Once TomTomNavigation is started, the active RoutePlan can be changed at any time—either manually or automatically by the navigation session.
To observe changes to the route during navigation, use the following listeners:
RouteUpdatedListener: triggered when the route is updated without a change in geometry. SeeRouteUpdatedReasonfor more details.RouteAddedListener: triggered when a new route is added to the session.RouteRemovedListener: triggered when a route is removed from the session.ActiveRouteChangedListener: triggered when a new route is selected as the active one. The route must already be added to the session.
To manually update the active RoutePlan call:
tomTomNavigation.setActiveRoutePlan(routePlan)
A manual
RoutePlanupdate results in aRouteAddedReason.ManuallyUpdatedreason provided in theRouteAddedListener.Other reasons can occur after route replanning.
1val routeAddedListener =2 RouteAddedListener { route: Route, options: RoutePlanningOptions, reason: RouteAddedReason ->3 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE4 }5val routeRemovedListener =6 RouteRemovedListener { route: Route, reason: RouteRemovedReason ->7 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE8 }9val activeRouteChangedListener =10 ActiveRouteChangedListener { route: Route ->11 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE12 }13val routeUpdatedListener =14 RouteUpdatedListener { route: Route, reason: RouteUpdatedReason ->15 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE16 }17tomTomNavigation.addRouteAddedListener(routeAddedListener)18tomTomNavigation.addRouteRemovedListener(routeRemovedListener)19tomTomNavigation.addActiveRouteChangedListener(activeRouteChangedListener)20tomTomNavigation.addRouteUpdatedListener(routeUpdatedListener)
To remove previously-added listeners, call the appropriate methods on the TomTomNavigation.
1tomTomNavigation.removeRouteAddedListener(routeAddedListener)2tomTomNavigation.removeRouteRemovedListener(routeRemovedListener)3tomTomNavigation.removeActiveRouteChangedListener(activeRouteChangedListener)4tomTomNavigation.removeRouteUpdatedListener(routeUpdatedListener)
Modifying the RoutePlanningOptions of the active route
The TomTom Navigation SDK offers extensions that allow users to modify the active route’s RoutePlanningOptions. These extensions are added to support the following use cases:
- Skipping an unvisited
RouteStop. Note: The final destination cannot be skipped. - Skipping a charging station using soft avoid. In this case, the
RoutePlannerattempts to calculate a route that avoids the specified charging station. However, if no reachable route can be found without visiting it, the station may still be included.
Skip route stop
To skip a route stop, retrieve the latest RoutePlanningOptions, replan the route, and update navigation using the setActiveRoutePlan method. The following snippet shows how to do this:
1val navigationSnapshot = tomTomNavigation.navigationSnapshot23val routeStopThatShouldBeSkipped =4 requireNotNull(navigationSnapshot!!.routes.first().waypoints.first()) {5 "Navigation should not be stopped and there should be a waypoint that the user wants to skip."6 }78// Create modified route planning options for the active route.9val modifiedRoutePlanningOptions =10 navigationSnapshot.currentActiveRoutePlanningOptions11 .skipRouteStop(routeStopThatShouldBeSkipped)1213// Plan a modified route and change the active route plan if successfully planned.14routePlanner.planRoute(modifiedRoutePlanningOptions).ifSuccess {15 // Choose a route, the first one is the best and usually fits the needs of the user.16 val chosenRoute = it.routes.first()1718 tomTomNavigation.setActiveRoutePlan(19 RoutePlan(20 route = chosenRoute,21 routePlanningOptions = modifiedRoutePlanningOptions,22 ),23 )24}.ifFailure {25 // Handle failure26}
Saving and resuming navigation
If the
NavigationVisualizationobject is used, make sure theNavigationResumeSnapshotRenewerobject is initialized after it.
Whether the app crashes, is accidentally terminated, or the system reclaims resources, saving an ongoing navigation session allows TomTomNavigation to restore its previous state when the app is restarted.
To support session restoration, TomTomNavigation provides the TomTomNavigation.navigationResumeSnapshot property and the TomTomNavigation.resume(navigationResumeSnapshot: NavigationResumeSnapshot) method. To serialize a NavigationResumeSnapshot, use the NavigationResumeSnapshot.serializeToFile(snapshotFle: File) or NavigationResumeSnapshot.serializeToBytes() methods. To deserialize it, use the NavigationResumeSnapshot.deserializeFromFile(file: File) or NavigationResumeSnapshot.deserializeFromBytes(data: byteArray) method.
You can save and resume a navigation session either automatically or manually.
Saving and resuming a navigation session automatically
To start saving navigation data automatically, create a default implementation of NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewer. Once navigation starts, a snapshot is saved periodically—every 30 seconds by default.
1val navigationResumeSnapshotRenewer =2 NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewerFactory.create(3 context = context,4 options = NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewerOptions(),5 tomTomNavigation = tomTomNavigation,6 )
The automatic saving interval is configured through NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewerOptionsas shown below:
1val options = NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewerOptions(saveInterval = 40.seconds)2val navigationResumeSnapshotRenewer =3 NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewerFactory.create(4 context = context,5 options = options,6 tomTomNavigation = tomTomNavigation,7 )
To automatically resume a previously saved session, use the NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewer.resumeNavigation() method:
1navigationResumeSnapshotRenewer.resumeNavigation(2 callback =3 object :4 Callback<NavigationResumeSnapshot, NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewerFailure> {5 override fun onSuccess(result: NavigationResumeSnapshot) {6 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE7 }89 override fun onFailure(failure: NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewerFailure) {10 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE11 }12 },13)
To resume a previously saved session manually, use the NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewer.latestNavigationResumeSnapshot() method:
1navigationResumeSnapshotRenewer.latestNavigationResumeSnapshot(2 callback =3 object :4 Callback<NavigationResumeSnapshot, NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewerFailure> {5 override fun onSuccess(result: NavigationResumeSnapshot) {6 tomTomNavigation.resume(result)7 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE8 }910 override fun onFailure(failure: NavigationResumeSnapshotRenewerFailure) {11 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE12 }13 },14)
Saving and resuming a navigation session manually
To manually save a NavigationResumeSnapshot to a file, use the following snippet:
1val fileName = "navigation_snapshot"2tomTomNavigation.navigationResumeSnapshot()3 .ifSuccess { snapshot ->4 snapshot.serializeToBytes() // or snapshot.serializeToFile(file)5 .ifSuccess { data ->6 val file = File(context.filesDir, fileName)7 FileOutputStream(file).use { fileOutputStream ->8 fileOutputStream.write(data)9 }10 }11 .ifFailure { failure: NavigationResumeSnapshotSerializationFailure ->12 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE13 }14 }15 .ifFailure { failure: NavigationResumeSnapshotFailure ->16 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE17 }
To resume a previously saved session from a file, use the following snippet:
1val fileName = "navigation_snapshot"2val file = File(context.filesDir, fileName)3if (file.exists()) {4 NavigationResumeSnapshot.deserializeFromFile(file)5 .ifSuccess { snapshot ->6 tomTomNavigation.resume(navigationResumeSnapshot = snapshot)7 }8 .ifFailure { failure: NavigationResumeSnapshotSerializationFailure ->9 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE10 }11}
After resuming, the
RouteAddedListeneris invoked with theRouteAddedReasonargument set toRouteAddedReason.NavigationResumed. TheTomTomNavigation.languageandTomTomNavigation.unitSystemare also restored from the previous session.You can apply a new language and unitSystem via the
TomTomNavigationobject after resuming the session.
To improve performance, save the NavigationResumeSnapshot after key events that result in significant changes to the navigation state, such as:
- Starting navigation along a route
- Refreshing the route
- Deviating from the route
- Visiting a waypoint
Route progress
Position-dependent fields that describe the user’s navigation status are collectively referred to as route progress data. Examples include the current position along the route (as an offset from the start), remaining travel time, and distance to the destination. These values are updated on every position update—typically once per second for each followed route. You can listen for changes to route progress. To listen for changes to route progress, set a ProgressUpdatedListener on the TomTomNavigation object. The ProgressUpdatedListener is triggered whenever the user’s progress along the Route changes. It provides a RouteProgressobject containing useful metrics such as estimated arrival time and remaining distance.
1val progressUpdatedListener =2 ProgressUpdatedListener { progress: RouteProgress ->3 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE4 }5tomTomNavigation.addProgressUpdatedListener(progressUpdatedListener)
To remove a previously added listener, call TomTomNavigation.removeProgressUpdatedListener(ProgressUpdatedListener).
tomTomNavigation.removeProgressUpdatedListener(progressUpdatedListener)
Route deviations
During navigation, the TomTomNavigation object tracks the user’s position relative to the navigated routes and determines which ones are currently being followed. To listen for updates about route tracking changes, use the RouteTrackingStateUpdatedListener.
This listener provides a RouteTrackingState object, which contains lists of followed and unfollowed routes. It also indicates whether the driver has deviated from all tracked routes. To verify if the driver deviated from the route, check if the RouteTrackingState.hasDeviated property is true.
To listen for the route tracking updates, set a RouteTrackingStateUpdatedListener on the TomTomNavigation object.
1val routeTrackingStateUpdatedListener =2 RouteTrackingStateUpdatedListener { routeTrackingState: RouteTrackingState ->3 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE4 }5tomTomNavigation.addRouteTrackingStateUpdatedListener(routeTrackingStateUpdatedListener)
To remove RouteTrackingStateUpdatedListener use the TomTomNavigation.removeRouteTrackingStateUpdatedListener(RouteTrackingStateUpdatedListener) method.
tomTomNavigation.removeRouteTrackingStateUpdatedListener(routeTrackingStateUpdatedListener)
If the driver deviates from the active route, navigation automatically enters free driving mode. In this mode, navigation temporarily operates without a RoutePlan. However, it automatically attempts to calculate a new route using the same cost model as the original. If successful, this new route becomes the active RoutePlan. You can find more details about automatic replanning in the Replanning on deviation section.
You can disable automatic replanning and manually provide a new
RoutePlanusing thesetActiveRoutePlan method.
Route guidance
The combination of maneuver instructions and maneuver announcements is called Route Guidance.
During navigation, TomTomNavigation generates guidance updates after each location change. These updates include upcoming maneuver instructions, the distance to the next maneuver, and announcements when the distance is within a triggerable range. All updates are sent to a GuidanceUpdatedListener. Note: Set the GuidanceUpdatedListener before starting the TomTomNavigation session.
The GuidanceUpdatedListener interface provides three callback methods:
onInstructionsChanged(List<GuidanceInstruction>)– Triggered when guidance instructions change. EachGuidanceInstructiondescribes a specific maneuver (e.g., Turn right, Keep left, Take the motorway).onAnnouncementGenerated(GuidanceAnnouncement, Boolean)– Triggered when an announcement is generated.
A GuidanceAnnouncement contains a message, geographic location, and distance to the instruction point. The shouldPlay flag indicates whether announcement should be triggered according to guidelines.
onDistanceToNextInstructionChanged(Distance, List<GuidanceInstruction>, InstructionPhase)– Triggered whenever the distance to the next instruction changes. It provides:- The current distance to the next maneuver (in meters)
- The list of upcoming instructions
- The current InstructionPhase
1val guidanceUpdatedListener =2 object : GuidanceUpdatedListener {3 override fun onInstructionsChanged(instructions: List<GuidanceInstruction>) {4 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE5 }67 override fun onAnnouncementGenerated(8 announcement: GuidanceAnnouncement,9 shouldPlay: Boolean,10 ) {11 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE12 }1314 override fun onDistanceToNextInstructionChanged(15 distance: Distance,16 instructions: List<GuidanceInstruction>,17 currentPhase: InstructionPhase,18 ) {19 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE20 }21 }22tomTomNavigation.addGuidanceUpdatedListener(guidanceUpdatedListener)
To remove a previously added GuidanceUpdatedListener, use the TomTomNavigation.removeGuidanceUpdatedListener(GuidanceUpdatedListener) method.
tomTomNavigation.removeGuidanceUpdatedListener(guidanceUpdatedListener)
To change the language used for guidance instructions, set the TomTomNavigation.preferredLanguage property:
tomTomNavigation.preferredLanguage = Locale.FRANCE
You can retrieve the current language using the TomTomNavigation.language property.
Lane-level guidance
TomTomNavigation has built-in support for generating lane guidance. Lane guidance is generated for each LaneSection object in a Route.
You can learn more about how to request a route with a LaneSection by reading the Route sections guide.
The LaneGuidance object includes:
lanes- A left‑to‑right list ofLaneobjects, each representing one physical lane on the road. EachLanecontains:directions- A list of possible driving directions available from the lane.
- Examples:
LEFT,STRAIGHT,RIGHT, etc. - At least one direction is expected.
follow- The recommended direction to follow if this lane is part of the active route.
nullmeans the lane is not recommended.- If not
null, the driver should follow that direction from this lane.
- More than one lane can be marked as recommended.
Example:
1// Only a left arrow, not recommended2Lane(3 directions = listOf(Direction.LEFT),4 follow = null,5)67// Straight + right arrows, straight is recommended8Lane(9 directions = listOf(Direction.STRAIGHT, Direction.RIGHT),10 follow = Direction.STRAIGHT,11)
laneSeparators- A list of separators (e.g., dashed lines, solid barriers) shown between and around lanes. For n lanes, n + 1 separators are provided. Each separator is shared between two lanes or marks the road edge.routeOffset- The distance from the start of the route to where this lane guidance begins.length- The distance over which this lane guidance is valid.
The following are the possible states for each individual lane guidance arrow
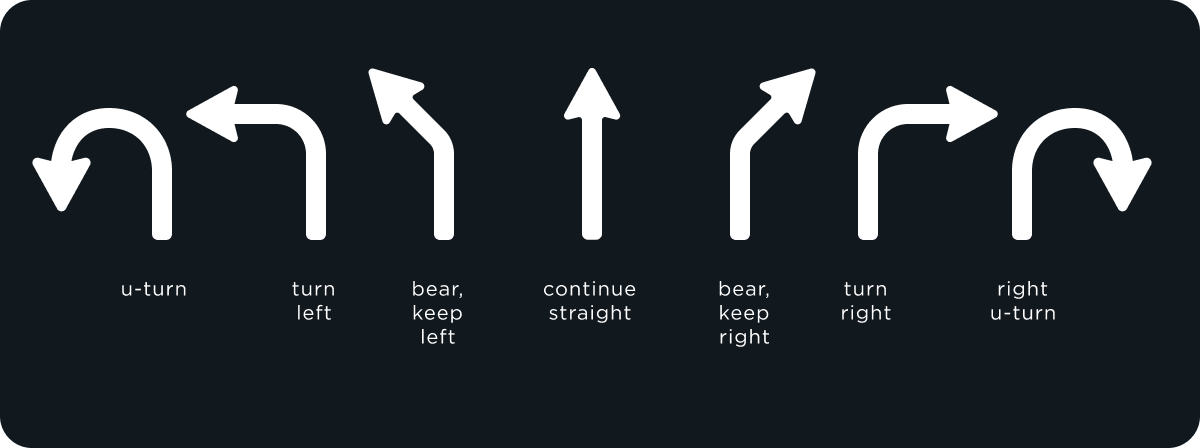
Highlighted SLG arrow represents the direction required by the current route. Greyed-out arrows represent alternative directions that should not be taken.
The following schematic images help illustrate Lane‑level Guidance:
- The right image shows the schematic lane arrow display, highlighting which lanes are part of the recommended maneuver. In this example, three right-turn lanes are highlighted.
- The left image provides a realistic visualization of the road ahead. It shows a highway segment with clearly visible lanes and lane separators, helping developers understand how the guidance maps to actual road structures.
The generated LaneGuidance is sent to LaneGuidanceUpdatedListener. LaneGuidanceUpdatedListener has two methods:
onLaneGuidanceStarted(LaneGuidance)- Triggered when lane guidance appears.onLaneGuidanceEnded(LaneGuidance)- Triggered when lane guidance disappears.
The onLaneGuidanceStarted(LaneGuidance) callback is only triggered when all of the following conditions are met:
- A maneuver is approaching (e.g., turn, merge, exit)
- More than one lane is available (
lanes.size > 1) - Each lane includes at least one direction
- At least one lane has a
followdirection - Not all lanes have a
followdirection
If these conditions are not met, the callback is not triggered.
1val laneGuidanceUpdatedListener =2 object : LaneGuidanceUpdatedListener {3 override fun onLaneGuidanceStarted(laneGuidance: LaneGuidance) {4 // laneGuidance.lanes is guaranteed to be non‑empty5 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE6 }78 override fun onLaneGuidanceEnded(laneGuidance: LaneGuidance) {9 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE10 }11 }12tomTomNavigation.addLaneGuidanceUpdatedListener(laneGuidanceUpdatedListener)
To remove a previously added LaneGuidanceUpdatedListener, use the TomTomNavigation.removeLaneGuidanceUpdatedListener(LaneGuidanceUpdateListener) method.
tomTomNavigation.removeLaneGuidanceUpdatedListener(laneGuidanceUpdatedListener)
Arrival experience
The Navigation module uses the generated RouteProgress to detect when the user arrives at their destination. When arrival is detected, the DestinationArrivalListener is triggered. This means that the ArrivalDetectionEngine has confirmed arrival.
Note: Even after arrival is detected, navigation remains in turn-by-turn mode until it is manually stopped.
To listen for arrival events, register a DestinationArrivalListener.
1val destinationArrivalListener =2 DestinationArrivalListener {3 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE4 }5tomTomNavigation.addDestinationArrivalListener(destinationArrivalListener)
To remove a previously registered DestinationArrivalListener, use:
tomTomNavigation.removeDestinationArrivalListener(destinationArrivalListener)
Waypoint arrival
The active Route may include intermediate stops that the driver intends to visit before reaching the final destination. These intermediate stops, known as waypoints, are listed in routeStops as instances of the RouteStop class. You can find more details on waypoints in the Waypoints and custom routes guide.
Arriving at a waypoint is detected in three phases: Approaching, Visiting, and Departing. When a waypoint’s arrival state changes, the WaypointArrivalListener is triggered. This means the ArrivalDetectionEngine has successfully detected arrival at the waypoint. It determines arrival by verifying whether the distance along the route is within the arrival radius of the waypoint. The distance threshold is:
- 100 meters on motorways
- 50 meters on other roads
A waypoint is automatically marked as departed when:
- The driver is on an active route and has increased the distance along the route by the distance threshold
- The driver deviates from the active route, moves away from the waypoint by more than the distance threshold in a straight line.
To listen for waypoint arrival and departure events, implement and register a WaypointArrivalListener:
1val waypointArrivalListener =2 object : WaypointArrivalListener {3 override fun onWaypointArrived(4 waypoint: RouteStop,5 route: Route,6 ) {7 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE8 }910 override fun onWaypointDeparted(11 waypoint: RouteStop,12 route: Route,13 ) {14 // YOUR CODE GOES HERE15 }16 }17tomTomNavigation.addWaypointArrivalListener(waypointArrivalListener)
To remove a previously added WaypointArrivalListener, use the following code:
tomTomNavigation.removeWaypointArrivalListener(waypointArrivalListener)
You can also manually mark a waypoint as visited independently of the ArrivalDetectionEngineby calling:
tomTomNavigation.departFromWaypoint(waypoint)
This method throws an exception if the specified waypoint has not yet been marked as arrived or has no effect if it has already been departed from.
If the operation succeeds, the WaypointArrivalListener.onWaypointDeparted callback is triggered. This signifies completion of arrival detection for the specific waypoint. Navigation then switches to detecting arrival for the next waypoint, if one exists.
Next steps
Since you have learned how to work with turn-by-turn navigation, here are recommendations for the next steps: