User location
The TomTom Map SDK allows you to show the current user location on the map. The location data is provided by the LocationProvider. The default implementation (DefaultCLLocationProvider) is provided by TomTom. CLLocationManager is used to obtain the user location. Learn more about existing location providers in the Built-in location providers.
To make it work you have to configure the following Purpose Strings in the Xcode build setting or in
Info.plist:NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription,NSLocationAlwaysAndWhenInUseUsageDescription. Omitting the correct key will lead to immediate authorization request failure, preventing the map from accessing the user’s location.
To display the current location button, please make sure to add the following line of code inside the onMapReady method. It is required to get the location.
1func mapView(_ mapView: MapView, onMapReady map: TomTomMap) {2 mapView.currentLocationButtonVisibilityPolicy = .hiddenWhenCentered3}
When the above steps are done, you should be able to display the current location. When the recenter button is pressed, the camera will move to the user’s current location.
Using the location provider with the map
Location updates are generated by the LocationProvider. DefaultCLLocationProvider is used to generate location updates. If you want to use a different location source or implement it according to your needs, your location provider needs to conform to LocationProvider. Here is an empty implementation that can be used as a template:
1class UserLocationProvider: LocationProvider {2 // It should be set to last known location.3 var lastKnownLocation: GeoLocation?45 func enable() {6 // Here you should enable location provider.7 // Might be called from private queue.8 }910 func disable() {11 // Here you should disable location provider.12 // After calling this method your location provider13 // should not provide any location updates.14 // Might be called from private queue.15 }1617 func addObserver(_: LocationUpdateObserver) {18 // Your location provider should support observer pattern.19 // Implementation should support multiple observers added at time.20 // Methods from `LocationUpdateObserver` should be called21 // each time new location data is available.22 }2324 func removeObserver(_: LocationUpdateObserver) {25 // This method should remove observer from observers list.26 }27}
Then it can be set and the map will start using it:
1let customProvider = UserLocationProvider()2map.locationProvider = customProvider3map.activateLocationProvider()
It will be used by the map to position the location marker according to the position updates.
You can also use the TomTomMap object to retrieve the currently used LocationProvider, and access the latest user location:
let lastLocation = map.locationProvider.lastKnownLocation
The location provider requires CLAuthorizationStatus.authorizedAlways or CLAuthorizationStatus.authorizedWhenInUse permissions. To get appropriate permissions, you must send authorization request by calling requestWhenInUseAuthorization() or requestAlwaysAuthorization() on the CLLocationManager instance respectively. Complete instructions to request location permissions on iOS can be found at Requesting authorization for location services.
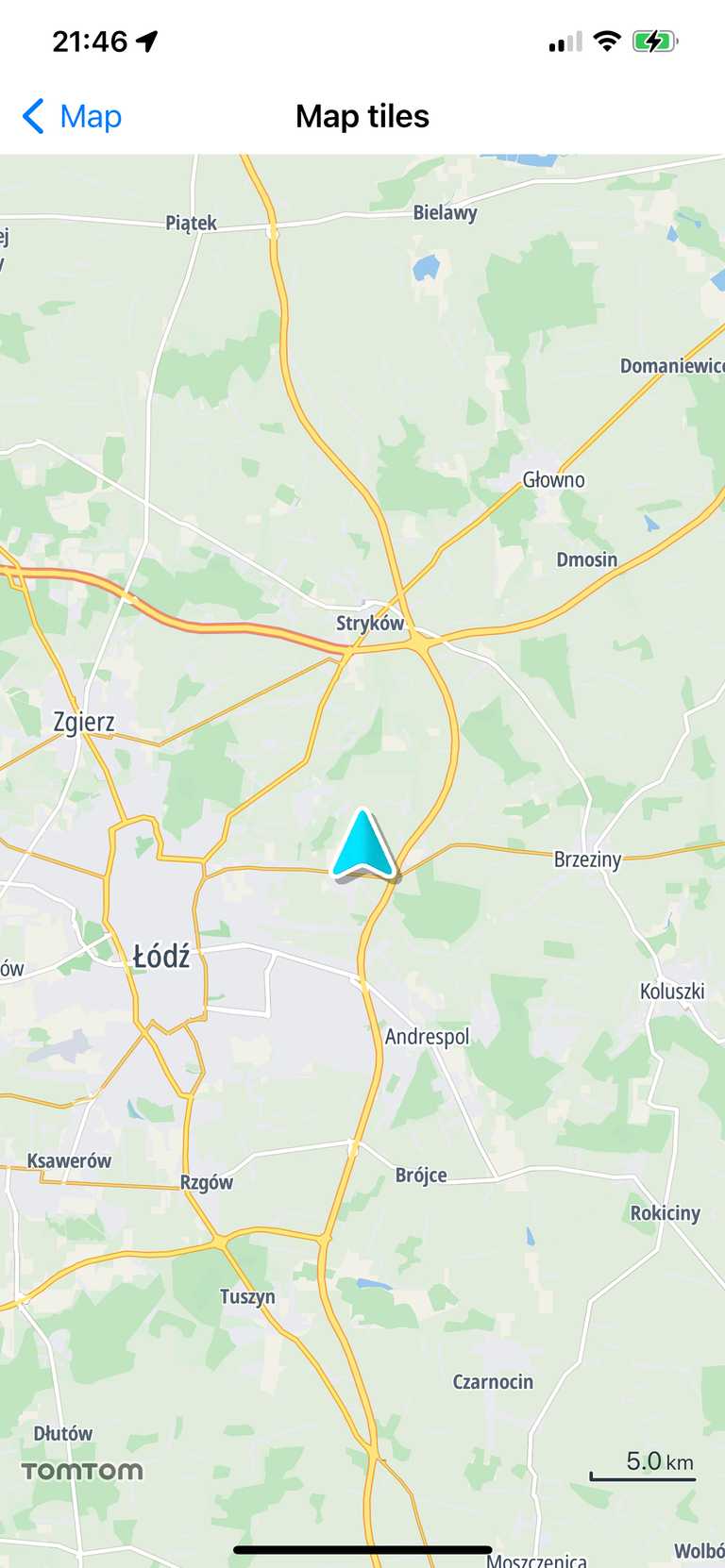
When the permissions granted, the user location will be shown as a navigation chevron on the map.
LocationIndicator
This parameter specifies the type of the marker.
The Map SDK provides two default markers with the ability to add a custom marker:
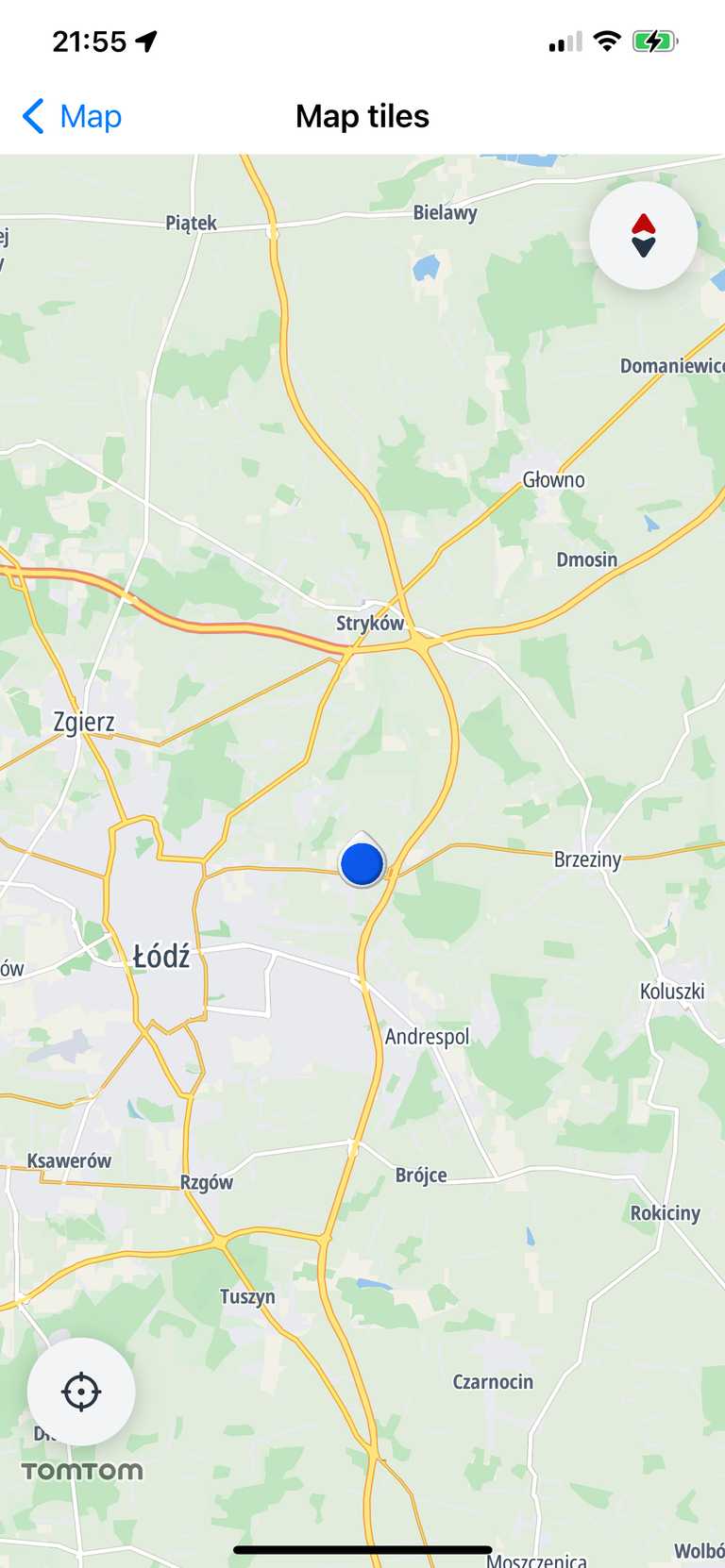
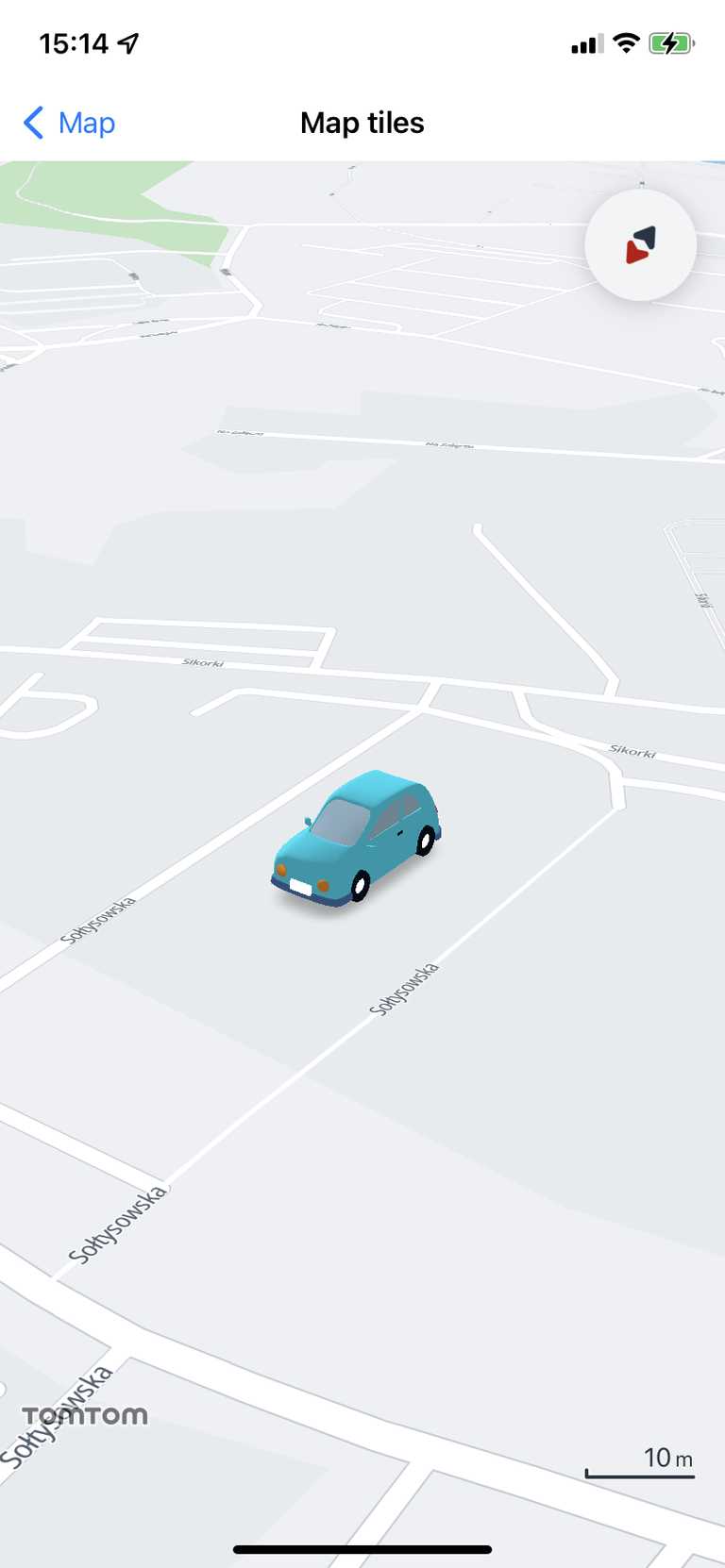
LocationIndicator.userLocation(scale:)- shows the user location pin.LocationIndicator.navigationChevron(scale:)- shows the navigation chevron.LocationIndicator.none- completely hides the location marker.LocationIndicator.custom(modelPath:scale:)- gives the ability to add a custom .glb model as a location indicator.
The location indicator is a LocationIndicator.navigationChevron by default. After the user authorizes the app to use their location, the chevron is displayed on the map.
To resize the location indicator, add a custom scale to LocationIndicator.userLocation(scale:) and LocationIndicator.navigationChevron(scale:).
map.locationIndicatorType = .userLocation(scale: 2.5)map.locationIndicatorType = .navigationChevron(scale: 2.5)
To switch from the default, set the appropriate value of LocationActions.locationIndicatorType.
1map.locationIndicatorType = .userLocation2map.locationIndicatorType = .navigationChevron3map.locationIndicatorType = .none4map.locationIndicatorType = .custom(modelPath: "asset://CUSTOM_MODEL.glb", scale: 10)
To add a custom location marker, specify a model path for the .glb file and specify a size. The project path that the custom model should be provided to is as follows: asset://file.glb. For more information about the model core requirements and supported features, refer to LocationIndicator.custom(modelPath:scale:).
map.locationIndicatorType = .custom(modelPath: "asset://car.glb", scale: 10)
Location marker click detection
The Map SDK provides a delegate method that can be used to receive onclick events performed on the location marker. If the user taps on the marker, the method from MapDelegate will be executed.
1extension UserLocationViewController: MapDelegate {2 func map(_ map: TomTomMap, onInteraction interaction: MapInteraction) {3 switch interaction {4 case let .tappedOnLocationMarker(coordinate):5 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */6 break7 default:8 break9 }10 }1112 func map(_ map: TomTomMap, onCameraEvent event: CameraEvent) {}13}
It provides the coordinate of the location on the map.