Show EV reachable range
Range visualization can be used to visualize a reachable range for electric vehicles (EVs) as well as combustion vehicles.
Before you start check Calculating a reachable range guide.
Project setup
Import the necessary frameworks using the following instructions, based on your preferred package manager:
Swift Package Manager
- Open your App’s target and navigate to General > Frameworks, Libraries, and Embedded Content.
- Add the following TomTomSDK libraries from the provided code snippet. Once the project is set up, import the mentioned frameworks into your code.
import TomTomSDKRangeVisualization
CocoaPods
- Add the
TomTomSDKRangeVisualizationmodule to your project’sPodfile1TOMTOM_SDK_VERSION = '0.71.1'23target 'YourAppTarget' do4 use_frameworks!5 pod 'TomTomSDKRangeVisualization', TOMTOM_SDK_VERSION6end - Install the dependencies by executing the following commands in the project directory:
pod repo-art update tomtom-sdk-cocoapodspod install --repo-update
- Import the
TomTomSDKRangeVisualizationframework:import TomTomSDKRangeVisualization
Initializing the Range Visualization module
Use the RangeVisualizationFactory method to create the rangevisualization object. It takes two arguments:
- tomTomMap: a
TomTomMapobject. - defaultRangeStyle: A default
RangeStylethat will be used for stylization of the range circles primitives
rangeVisualization = RangeVisualizationFactory.create(map: tomtomMap, style: defaultRangeVisaulizationStyle)
Displaying a reachable range
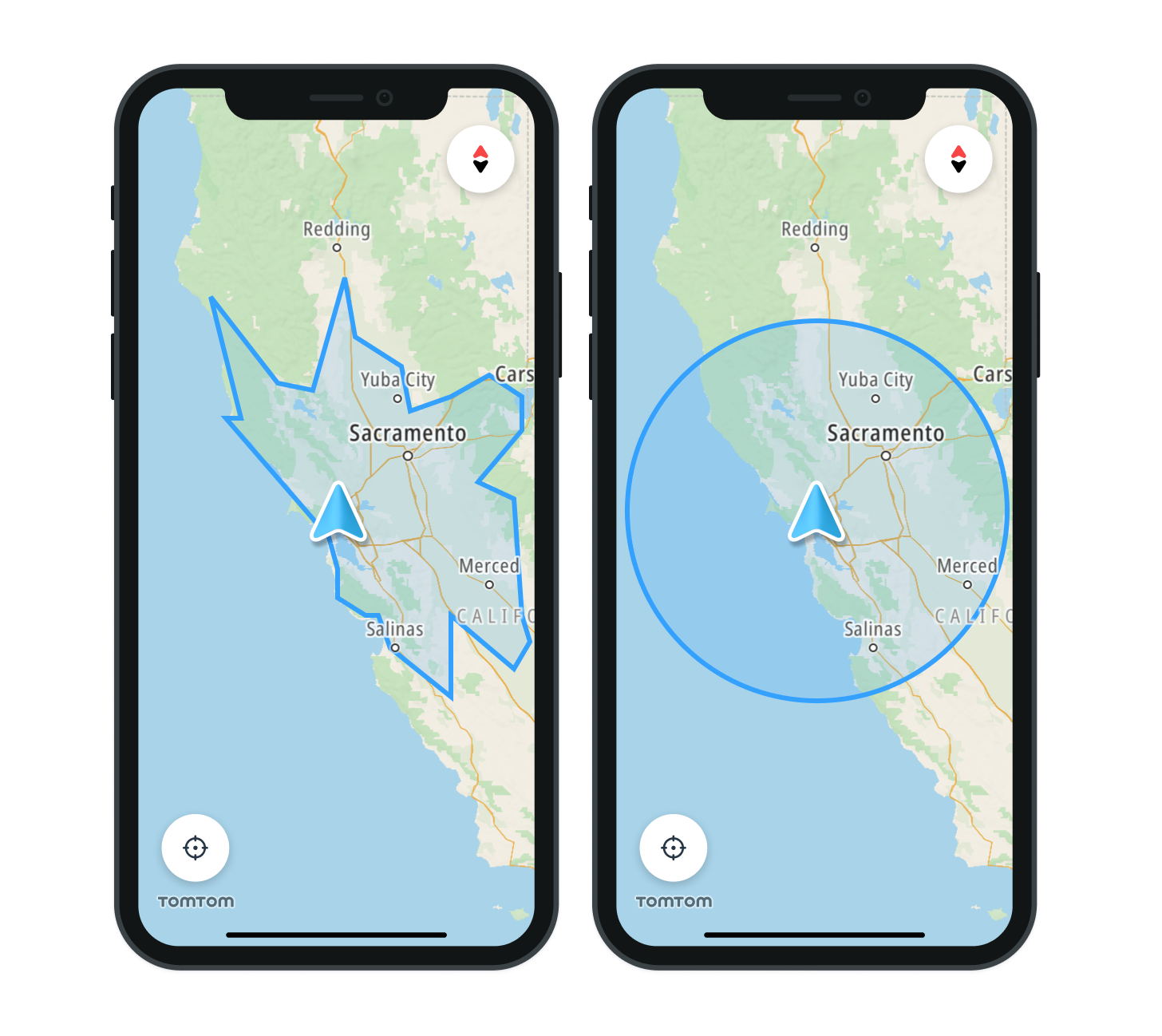
There are two ways to visualize a range on the map: . Circle - used to display a range as a reachable radius . Polygon - used to display a more detailed range
To display a reachable range, a Range object must be created and passed to the display method of RangeVisualization. Choose between two types of Range objects: NamedPolygon and NamedCircle
1let namedCircle1 = NamedCircle(name: name1, origin: origin1, radius: radius1)2let namedCircle2 = NamedCircle(name: name2, origin: origin2, radius: radius2)34let circleRange = Range.namedCircles([namedCircle1, namedCircle2])5rangeVisualization.display(range: circleRange)
1if case let .polygon(points1) = calculateRangeResponse.boundaries[Budget.energy(amount: Measurement.tt.kilowattHours(5))],2 case let .polygon(points2) = calculateRangeResponse3 .boundaries[Budget.energy(amount: Measurement.tt.kilowattHours(10))] {4 let namedPolygon1 = NamedPolygon(name: name1, boundary: points1)5 let namedPolygon2 = NamedPolygon(name: name2, boundary: points2)6 let polygonRange = Range.namedPolygons([namedPolygon1, namedPolygon2])7 rangeVisualization.display(range: polygonRange)8}
Clearing the range
The range currently being visualized on the map can be cleared using the clear method of RangeVisualization:
rangeVisualization.clear()
Learn more
Since you have learned how to display Reachable range, here are recommendations for the next steps: