Modularization
The Navigation SDK for iOS is only available upon request. Contact Sales to get started.
The architecture of the TomTom SDKs is modular, meaning that each navigation component is independent of the others.
As a result of this modularization, components are easily replaced with ones from other sources or omitted when they are not needed. Modularity makes it easier to change the standard SDK to address a specific use case.
These replaceable components are referred to as engines.
Orchestrator
The Navigation module depends on engines to orchestrate a pipeline after each location update. The location updates are supplied by the LocationProvider. You can read more about the LocationProvider API used by the navigation in the Location tracking[Location tracking] guide. If the LocationProvider doesn’t provide a new location, the system falls back to dead reckoning after few seconds.
On each processing pipeline, snapshots of engines are captured and utilized at various stages of the navigation flow, as demonstrated in the following diagram.
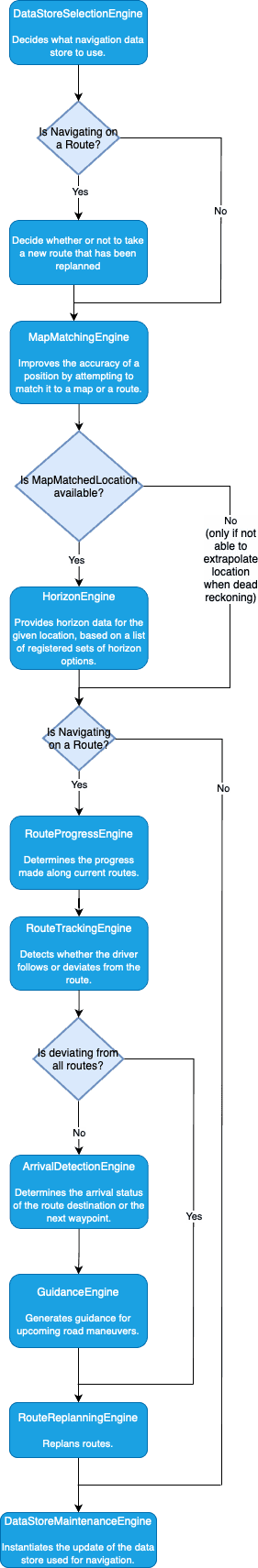
Engines
The orchestrator works with the following engines:
DataSourceSelectionEngine- Decides which navigation data store is used in the next navigation cycle. This is only relevant for hybrid mode.MapMatchingEngine- Improves the accuracy of a position by attempting to match it to a map or a route.HorizonEngine- Provides horizon data for the given location, based on a list of registered sets of horizon options.RouteProgressEngine- Determines the progress made so far along the current route.RouteTrackingEngine- Detects whether the driver is tracking a route.ArrivalDetectionEngine- Verifies if the destination or the next waypoint has been reached during navigation.GuidanceEngine- Generates guidance for upcoming road maneuvers.RouteReplanningEngine- Replans routes.DataStoreMaintenanceEngine- Instantiates the update of the data store used for navigation.
Customized engines are specified in two ways:
- During creation of the configuration object for the selected mode:
- Dynamically on an existing
TomTomNavigationobject usingNavigationEngineRegistry.
1tomTomNavigation.navigationEngineRegistry.updateEngines(2 mapMatchingEngine: customMapMatchingEngine,3 routeReplanningEngine: customRouteReplanningEngine,4 guidanceEngine: customGuidanceEngine,5 horizonEngine: customHorizonEngine,6 routeTrackingEngine: customRouteTrackingEngine,7 routeProgressEngine: customRouteProgressEngine,8 arrivalDetectionEngine: customArrivalDetectionEngine,9 dataStoreMaintenanceEngine: customDataStoreMaintenanceEngine,10 dataSourceSelectionEngine: customDataSourceSelectionEngine11)
Navigation snapshot
Navigation session data is passed between different engines and pipeline iterations using the NavigationSnapshot.
The snapshot doesn’t contain all session data, just what other engines need as input (e.g., the RouteProgressEngine uses the MapMatchingResult to calculate the progress along the route). You can see the order that engines use data in the description of the orchestrator.
Because it provides other engines with input data, the navigation snapshot always contains current information about the navigation session, such as current location, matched location, and progress along a route. It is updated whenever new values are available.
The data is divided into the following classes:
LocationSnapshot- contains information specific to location e.g., theMapMatchingResult.ConfigurationSnapshot- the navigation configuration, e.g., theUnitsSystemused for guidance.Vehicle- the current vehicle profile.TripSnapshot- information about the current trip session, e.g., whether the driver deviated from the route or reached the destination.RouteSnapshot- route-specific data such as theRoutePlan,RouteProgress, or visited waypoints.
The current navigation snapshot can be accessed using the TomTomNavigation.navigationSnapshot property. Note that the snapshot is nil if the navigation is not yet started or has already been stopped.
Next steps
Since you have learned about our modular architecture, here are recommendations for the next steps: