Traffic Flow - DATEX II
Purpose
The TomTom Traffic Flow - Intermediate Service - DATEX II (hereafter called 'Service') is designed for server-to-server integration with traffic control center, routing, navigation, and mapping applications. It contains real-time travel times and speeds for segments, based on TomTom's Traffic technology, with several possible configurations.
This document describes the data exchange method and the payload description of the Service interface.
Important
TomTom only supports the Intermediate Service with the use of the TomTom customized DATEX II schema, available for download from our website (linked previously and later in this document). Using the Service with the standard DATEX II schema will disable the functionality that is included with the Service. Therefore, the standard DATEX II schema is not supported.
Scope
This document gives basic information on the Service and shows how to configure it to work with your environment. The user is expected to have basic installation knowledge and experience using XML-based schemas.
Intended audience
This document is intended to be used by TomTom partners and customers (decision makers and developers).
Features
TomTom offers traffic flow data to customers. A custom product is configured based upon your specific needs. The product is static, so included regions and features are fixed (once the product is configured). Detailed information about the default enabled features and their representation in DATEX II can be found in the section Default enabled information, but it also provides customizable configuration options (see section Optionally activatable features).
Request data
The Service uses RESTful API (Representation State Transfer) technology. Since you only need to use one URL, the Service is relatively uncomplicated to use.
'Simple HTTP server' profile
The interface supports the client pull method, also known as the simple HTTP server profile. The profile is described in the Software Developers Guide and Exchange Platform Specific Model (see the DATEX II payload specification for the links to the documents). TomTom does not support the SOAP envelope, as described in the Software Developers Guide.
Important
To use this Service, ensure that all prerequisites are met as described in the section A secure connection or at Authentication for client certificate access.
HTTPS Method: GET
For ease of viewing and identification:
- Constants and parameters enclosed in curly brackets { } must be replaced with their values.
- Please see the following Request parameters section with the required and optional parameters tables for their values.
The sample URL is formatted as follows:
https://{baseURL}/tsq/hdf/{productName}/{apiKey}/content.xml[?flowType={flowType}]
The following is an example URL:
https://cert-traffic.tomtom.com/tsq/hdf/DEU-OPENLR/{Your_API_Key}/content.xml
The following is an example cURL request:
curl --compressed -XGET 'https://cert-traffic.tomtom.com/tsq/hdf/DEU-OPENLR/{Your_API_Key}/content.xml'
Request parameters
The following table provides a detailed explanation of the available fields that were previously shown.
| Required parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Base URL for calling the API. |
| Name of the product (feed) you are requesting.
These will be indicated to you as part of the
provisioning process. Typically, it explains the
country (country code), and the location referencing
method (see Location referencing). |
| Authorization key for access to the API. |
| Optional parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| When the feed is requested without the parameter
When using this parameter, at the first request the free-flow
information should be downloaded. Afterwards, non-free-flow
information can be downloaded for each future request.
The free-flow and non-free-flow data are related.
The segments for both files should be in sync, otherwise there
is a mismatch in the locations of the free-flow data. The verification is done by confirming the |
Request headers
Since flow feeds can be very large, TomTom recommends optimizing the information transmission as much as possible. Through optimization, the client receives more up-to-date information.
All responses will be gzip compressed as it significantly reduces the payload size. The use of the HTTP header
Accept-Encodingis required. For more information see our page about Gzip compression.
| Headers | Description |
|---|---|
| If-Modified-Since | TomTom recommends using the standard HTTP header
|
Response data
Response codes
| Response code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 OK | Indicates that the request has succeeded. The response body will contain the requested data. |
| 304 Not Modified | Only used if the |
| 401 Unauthorized | Indicates that the request requires user authentication information. The client MAY repeat the request with a suitable Authorization header field. |
| 406 Not Acceptable | The server doesn't find any content that conforms with the |
Response example
If you make the following request:
https://cert-traffic.tomtom.com/tsq/hdf/DEU-OPENLR/{Your_API_Key}/content.proto?flowType=nff
You can expect a response that contains DATEX II XML data that could look like this:
1<?xml version="1.0"?>2<d2LogicalModel xmlns="http://datex2.eu/schema/1_0/1_0" modelBaseVersion="1.0">3 <exchange>4 <supplierIdentification>5 <country>nl</country>6 <nationalIdentifier>TomTom Traffic Service</nationalIdentifier>7 </supplierIdentification>8 </exchange>9 <payloadPublication xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"10 xsi:type="ElaboratedDataPublication" lang="en">11 <publicationTime>2015-12-23T11:54:00Z</publicationTime>12 <publicationCreator>13 <country>other</country>14 <nationalIdentifier>db14af1d-3827-4d61-8525-8f70bc1c5b3f15e87601</nationalIdentifier>15 </publicationCreator>16 <headerInformation>17 <confidentiality>internalUse</confidentiality>18 <informationStatus>real</informationStatus>19 </headerInformation>20 <referenceSettings>21 <locationSetReference/>22 </referenceSettings>23 <elaboratedData id="Ob719eb226ba9b25e44b15b17">24 <basicDataValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="TravelTimeValue">25 <supplierCalculatedDataQuality>95.0</supplierCalculatedDataQuality>26 <affectedLocation>27 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="LocationByReference">28 <locationExtension>29 <openlr>30 <binary>CwcZ6yJrqQslDgRLAQULFw==</binary>31 </openlr>32 </locationExtension>33 <predefinedLocationReference>OpenLR</predefinedLocationReference>34 </locationContainedInGroup>35 </affectedLocation>36 <travelTime>346.0</travelTime>37 <travelTimeValueExtension>38 <averageSpeed>9.0</averageSpeed>39 <relativeSpeed>0.257</relativeSpeed>40 <trafficCondition>queuingTraffic</trafficCondition>41 </travelTimeValueExtension>42 </basicDataValue>43 </elaboratedData>44 [...]45 </payloadPublication>46</d2LogicalModel>
Response - DATEX II payload specification (analysis of the received output)
The payload in the output is formatted as DATEX II, which is a European standard for the exchange of Traffic and Travel Information. TomTom supports version 1. Recommended documents are:
- DATEX II v1.0 User Guide version 1.0 ( DATEXIIv1.0-UserGuide_v1.0.pdf )
- DATEX II v1.0 Software Developers Guide version 1.0 ( DATEXIIv1.0-DevGuide_v1.0.pdf )
- DATEX II v1.0 Exchange Platform Specific Model version 1.0 ( DATEXIIv1.0-ExchangePSM_v1.0.pdf )
- A browsable DATEX II version 1.0 data dictionary ( DATEXIIv1.0-DataDictionnary_v1.0.zip )
The Elaborated Data Publication, used by TomTom, is described in more detail in section 4.11 of the DATEX II User Guide version 1.0.
Important: XSD schema
TomTom extended the data model with additional fields; the full XSD schema including extensions can be downloaded by clicking this Level B extension. It is a "Level B" extension of the standard XML schema: DATEXIISchema_1_0_1_0.xsd. Such an extension is interoperable with the "Level A" data model (see section 2.2.3 in the DATEX II User Guide version 1.0 for more information).
Default enabled information
ElaboratedData message default information
For every segment, speed and travel-time information and location information (see also Location referencing) is provided. Depending on whether the traffic on a segment is flowing freely (also referred to as freeflow) or whether it is congested (also referred to as non-freeflow), different combinations of DATEX II fields are used.
Free-flow message
A free-flow message consists of the following default information:
freeFlowSpeed: The freeflow speed in km/h that is expected under ideal freeflow conditions.freeFlowTravelTime: The travel time in seconds that is expected under ideal freeflow conditions.supplierCalculatedDataQuality: A measure of data quality assigned to the value by the supplier. Freeflow messages use 100%. See SupplierCalculatedDataQuality for more information.affectedLocation: The definition of a segment of a road in a particular direction. See Location reference for more information.
A typical freeflow message looks as follow:
1<elaboratedData id=[...]>2 <basicDataValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="TravelTimeValue">3 <supplierCalculatedDataQuality>100.0</supplierCalculatedDataQuality>4 <affectedLocation>5 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="LocationByReference">6 <locationExtension>7 <openlr>8 <binary>CwmH0SVZpiurBQCGAPErDw==</binary>9 </openlr>10 </locationExtension>11 <predefinedLocationReference>OpenLR</predefinedLocationReference>12 </locationContainedInGroup>13 </affectedLocation>14 <freeFlowSpeed>24.0</freeFlowSpeed>15 <freeFlowTravelTime>46.2</freeFlowTravelTime>16 </basicDataValue>17</elaboratedData>
Non-freeflow message
A non-freeflow message consists of the following default information:
averageSpeed: The current average speed in km/h on the affected location.travelTime: Current average travel time in seconds based on real-time measurements on theaffectedLocation.supplierCalculatedDataQuality: A measure of data quality assigned to the value by the supplier. 100% equates to perfect quality. See SupplierCalculatedDataQuality for more information.affectedLocation: The definition of a segment of a road in a particular direction. See Location reference for more information.
If the affected location is closed, the
averageSpeedis set to 0 km/h and thetravelTimerefers to the travel time under free-flow conditions.
A typical non-freeflow message looks as follows:
1<elaboratedData id=[...]>2 <basicDataValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="TravelTimeValue">3 <supplierCalculatedDataQuality>74.0</supplierCalculatedDataQuality>4 <affectedLocation>5 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="LocationByReference">6 <locationExtension>7 <openlr>8 <binary>CwmIdSVX4yusBQEn/zYrHA==</binary>9 </openlr>10 </locationExtension>11 <predefinedLocationReference>OpenLR</predefinedLocationReference>12 </locationContainedInGroup>13 </affectedLocation>14 <travelTime>30.96</travelTime>15 <travelTimeValueExtension>16 <averageSpeed>0.0</averageSpeed>17 </travelTimeValueExtension>18 </basicDataValue>19</elaboratedData>
SupplierCalculatedDataQuality
This field contains a quality measure for the provided travel time and speed. It is based on the following variables:
- The number of real-time measurements from devices driving the affected locations at the moment.
- The standard deviation of the measurements.
- The percentage of the affected location that is covered with measurements.
- Compatibility of measurements with historic data.
- The age of the measurements.
When we determine that an insufficient amount of real-time measurements are available, historic data
is given a greater weight in the travel time estimate. If the value of
supplierCalculatedDataQualityis below 60% (0.6), then the historic data holds greater
importance in the calculation. A value of 50% (0.5) implies that the provided travel time is based
only on the historic speed profile.
Location referencing
Geographical representation of the road segments is an important part of the payload. There are two geographical representations that are supported: TMC and OpenLR. Since OpenLR prevents interpretation differences, licensing costs, map dependencies, or version dependencies, TomTom recommends using OpenLR instead of TMC. TMC based data is still offered for customers with existing platforms that need compatibility with their legacy systems.
The data type of the affectedLocation in the schema is a Group of Locations. LocationByReference is
the location method used, and it contains the identifier of a predefinedLocationReference. If we use
TMC, the predefinedLocationReference is a TMC link identifier. If we use OpenLR, the actual location
reference information is provided in TomTom’s proprietary extension LocationExtensionType and the
predefinedLocationReference is constantly set to “OpenLR.”
| Location referencing method | Example |
|---|---|
| OpenLR |
|
| TMC |
|
OpenLR
OpenLR is a dynamic location referencing method that allows referencing of any road on the complete digital map. Because of its flexibility, it is possible to describe traffic events on high-level and lower-level road classes that are usually not covered by TMC. The method is available free of charge. The service uses binary format version 3, as described in the OpenLR whitepaper. The whitepaper, software developer kit, and open source reference implementations are available for download from the OpenLR website. TomTom offers support for third parties to implement and test their own implementations.
Traffic Message Channel (TMC)
When using TMC as a geographical representation, travel times are measured by a TMC link. A TMC link is part of a TMC path. A TMC link is a sequence of road elements that starts at a TMC location, and ends at the next TMC location in the TMC table in the specified direction. You can recognize a TMC link by:
- TMC table (country code, location table number, version).
- Primary TMC location, defining the TMC point location at the end of the TMC link.
- Direction, as defined by the TMC path.
- An optional extent (the default value is 1).
Generally, the set of TMC link identifiers that can be used in an ElaboratedDataPublication is static. That
means that in subsequent ElaboratedDataPublications, the same locations are used. However, this is not always the
situation. Sometimes, the set of the TMC link identifiers that are used can be changed. These
changes occur when a new TMC table is introduced.
referenceSettings
For TMC-based data, the referenceSettings contain a locationSetReference. Here, a reference is
made to a specific version of a TMC location table. The format is: A + BB + "v" + C + "." + D,
where:
A= the Country Code (hex format).BB= the Location Table Number (2 digits).C= the major version number (1 or 2 digits).D= the minor version number (1 or 2 digits).
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>2<d2LogicalModel xmlns="http://datex2.eu/schema/1_0/1_0" modelBaseVersion="1.0">3 <exchange>4 <supplierIdentification>5 <country>nl</country>6 <nationalIdentifier>TomTom Traffic Service</nationalIdentifier>7 </supplierIdentification>8 </exchange>9 <payloadPublication xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="ElaboratedDataPublication" lang="en">19 <referenceSettings>20 <locationSetReference>D01v22.0</locationSetReference>21 </referenceSettings>22 <!-- list of elaborated data elements follows -->23 [...]24 <payloadPublication>25</d2LogicalModel>
TMC link identifier
In TMC–based DATEXII, TMC chain information includes the following parts ACVVDLLLLL[xE[E]]:
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
A | Fixed letter 'L' |
C | Hexadecimal country code as described in IEC 62106. |
VV | This is the TMC Location Table code. |
D | TMC direction of the chain (defined by the TMC path). For possible values, see TMC direction. |
LLLLL | TMC point location code. If the number is not five digits long, zeros are added at the beginning until there are five digits. |
[xE[E]] | Either empty, when extent = 1, or fixed letter |
Using the specified TMC table, the secondary location (start of the stretch) can be found from the
primary location, the direction, and the extent. C, VV, and LLLLL correspond with the TMC Location
Reference that is a unique identifier for a TMC location.
TMC direction
The possible values for D infer the direction of travel (secondary to primary location) along the
TMC path.
| Value | Direction |
|---|---|
p | Positive |
n | Negative |
TMC examples
In this section, we demonstrate how to resolve TMC link identifiers on the receiver side. Here, we map the definition of each of the fields within the link identifier, and provide guidance on using the extent to find the secondary location.
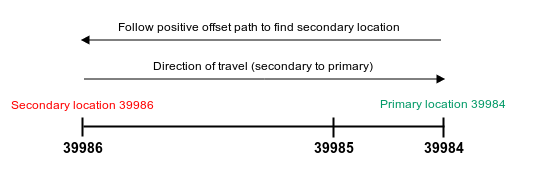
Example 1: L817n39984x2
Given the TMC location data:
- Country code: 8
- Location table number: 17
- Direction from secondary to primary location: negative
- Primary location ID: 39984
- Extent: 2
Interpret the TMC location data to resolve the secondary location:
- Invert direction: negative → positive.
- Since the resolved direction is positive, follow the positive offset path for 39984 in the TMC table for two extents.
- You will find the subsequent positive offsets are 39985 and 39986, therefore, the resolved secondary location is 39986.
Example 2: LD01p27442
Given the TMC location data:
- Country code: D
- Location table number: 1
- Direction from secondary to primary location: positive
- Primary location ID: 27442
- Extent: 1 (if the extent is not provided explicitly, then it is 1)
Interpret the TMC location data to resolve the secondary location:
- Invert direction: positive → negative.
- Since the resolved direction is negative, follow the negative offset path for 27442 in the TMC table for one extent.
- You will find the subsequent negative offset is 30080.

Predefined Location Product
In DATEX II, a PredefinedLocationsPublication is used to predefine a set of locations, that can then
be referred to in the elaboratedDataPublication. This allows for simplification of the
elaborated data publication, where typically, the elaborated data is published for a fixed set of
locations that is then published separately. However, since there is a straightforward relationship
between the predefined location reference we use, and the corresponding TMC link, the Predefined
Location Product is not published.
Optionally activatable features
The DATEX II data model has been extended to allow additional parameters. The Service has the following possible extensions.
Miles per hour
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | The current average speed in miles per hour. |
1<elaboratedData id="[...]">2 <basicDataValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="TravelTimeValue">15 <travelTimeValueExtension>16 <averageSpeed>16.8</averageSpeed>17 <averageSpeedInMPH>10.44</averageSpeedInMPH>18 </travelTimeValueExtension>19 </basicDataValue>20</elaboratedData>
Relative speed
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | The relative speed is the relationship between the average speed and the free-flow speed.
The range is from 0 to 1 and is precise to three decimal places.
If the value is |
1<elaboratedData id="[...]">2 <basicDataValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="TravelTimeValue">15 <travelTimeValueExtension>16 <averageSpeed>9.1</averageSpeed>17 <relativeSpeed>0.314</relativeSpeed>18 </travelTimeValueExtension>19 </basicDataValue>20</elaboratedData>
Traffic condition
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Traffic status according to the relative speed of the location and it can be any of the following values (see more details on FAQ about the definition of traffic conditions):
|
1<elaboratedData id="[...]">2 <basicDataValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="TravelTimeValue">15 <travelTimeValueExtension>16 <averageSpeed>5.4</averageSpeed>17 <trafficCondition>stationaryTraffic</trafficCondition>18 </travelTimeValueExtension>19 </basicDataValue>20</elaboratedData>
Map version
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | This option provides the names and versions of the maps that were used to create the content. |
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>2<d2LogicalModel xmlns="http://datex2.eu/schema/1_0/1_0" modelBaseVersion="1.0">3 <exchange>4 <supplierIdentification>5 <country>nl</country>6 <nationalIdentifier>TomTom Traffic Service</nationalIdentifier>7 </supplierIdentification>8 </exchange>9 <payloadPublication xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="ElaboratedDataPublication" lang="en">10 <publicationTime>2025-02-24T15:20:05Z</publicationTime>11 <publicationCreator>12 <country>other</country>13 <nationalIdentifier>f8d19def-5830-42df-bbc9-a68136294e3dd94cfde</nationalIdentifier>14 </publicationCreator>15 <payloadPublicationExtension>16 <mapVersion>eur2025.03.002</mapVersion>17 </payloadPublicationExtension>18 [...]19 <!-- list of elaborated data elements follows -->20 [...]21 </payloadPublication>22</d2LogicalModel>