Traffic Incidents - DATEX II
Important notes:
- This TomTom Orbis API is in public preview.
- This API is powered by the TomTom Orbis Maps.
- See the TomTom Orbis Maps documentation for more information.
Purpose
The TomTom Traffic Incidents - Intermediate Service - DATEX II (hereafter called 'Service') is based on DATEX II v1.0. DATEX II is a standard for information exchange between traffic control centers, service providers, and application developers.
The Service provides the latest real-time information about traffic incidents, their causes and impacts on travelers. Typical traffic incidents include accidents, road construction projects, traffic jams, road closures, and any other road-related situation that could potentially cause a delay.
In this document, we discuss how to access the Service and the features that are included.
Important
TomTom only supports the Intermediate Service with the use of the TomTom customized DATEX II schema, available for download from our website (linked previously and later in this document). Using the Service with the standard DATEX II schema will disable the functionality that is included with the Service. Therefore, the standard DATEX II schema is not supported.
Scope
This document gives basic information on the Service and shows how to configure it to work with your environment. Basic knowledge of installing and using XML-based schemas is necessary.
Intended audience
This information is intended to be used by TomTom partners and customers (decision makers and developers).
Features
TomTom offers traffic incident data to customers. In the basic configuration, TomTom provides customers information on traffic congestion and other roadwork-related traffic events.
Each traffic incident is represented in a DATEX II event, and we add an Alert-C event code with the same meaning. This Alert-C event code allows the user to customize the content at their own discretion. This information is organized by country-based datasets. The product is static. This means that the included regions and features are fixed once the product is configured. Products are customer-specific.
Detailed information about the default enabled features and their representation in DATEX II can be found in the section Default enabled information.
The Service provides users traffic incident data with a highly customizable optional configuration, in addition to the features enabled by default. The section Optionally activatable features provides detailed information about these configurations and their representation in DATEX II.
Request data
The Service uses RESTful API (Representation State Transfer) technology. Since you only need to use one URL, the Service is relatively uncomplicated to use.
'Simple HTTP server' profile
The interface supports the client pull method, also known as the simple HTTP server profile. The profile is described in the Software Developers Guide and Exchange Platform Specific Model (see the DATEX II payload specification for the links to the documents). TomTom does not support the SOAP envelope as described in the Software Developers Guide.
Important
To use this service, ensure that all prerequisites are met as described in the section, A secure connection or at Authentication for client certificate access.
How do you make a request?
To make a request, the URL should be constructed as shown in the following sections.
HTTPS Method: GET
For ease of viewing and identification:
- Constants and parameters enclosed in curly brackets { } must be replaced with their values.
- Please see the following Request parameters section with the required and optional parameters tables for their values. The generic request format is as follows.
The sample URL is formatted as follows:
https://{baseURL}/tsq/hdt/{productName}/{apiKey}/content.xml
The following is an example URL:
https://cert-traffic.tomtom.com/tsq/hdt/DEU-HDT-OPENLR/{Your_API_Key}/content.xml
The following is an example cURL request:
curl --compressed -XGET 'https://cert-traffic.tomtom.com/tsq/hdt/DEU-HDT-OPENLR/{Your_API_Key}/content.xml'
Request parameters
The following table provides a detailed explanation of the available fields that were previously
shown in the HTTPS Method: GET section.
| Required parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Base URL for calling the API. |
| Name of the product (feed) you are requesting.
These will be indicated to you as part of the
provisioning process. Typically, it explains the
country (country code), and the location referencing
method (see Location, |
| Authorization key for access to the API. |
Request headers
Since incident feeds can be very large, TomTom recommends optimizing the information transmission as much as possible. By doing this, the client receives more up-to-date information.
All responses will be gzip compressed as it significantly reduces the payload size. The use of the HTTP header
Accept-Encodingis required. For more information see our page about Gzip compression.
| Headers | Description |
|---|---|
| If-Modified-Since | TomTom recommends using the standard HTTP header
|
Response data
Response codes
| Response code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 OK | Indicates that the request has succeeded. The response body will contain the requested data. |
| 304 Not Modified | Only used if the |
| 401 Unauthorized | Indicates that the request requires user authentication information. The client MAY repeat the request with a suitable Authorization header field. |
| 406 Not Acceptable | The server doesn't find any content that conforms with the |
Response example
This is a response you receive after a request is made. If you make the following request:
https://cert-traffic.tomtom.com/tsq/hdt/DEU-HDT-OPENLR/{Your_API_Key}/content.xml
You can expect the following response:
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>2<d2LogicalModel xmlns="http://datex2.eu/schema/1_0/1_0" modelBaseVersion="1.0">3 <exchange>4 <supplierIdentification>5 <country>nl</country>6 <nationalIdentifier>TomTom Traffic Service</nationalIdentifier>7 </supplierIdentification>8 </exchange>9 <payloadPublication xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="SituationPublication" lang="en">10 <publicationTime>2023-10-10T12:44:30Z</publicationTime>11 <publicationCreator>12 <country>other</country>13 <nationalIdentifier>71553ccb-728e-4ee3-9717-4afd308ce0f3</nationalIdentifier>14 </publicationCreator>15 <situation id="TTI-71553ccb-728e-4ee3-9717-4afd308ce0f3-TTL25838637712020000">16 <headerInformation>17 <confidentiality>internalUse</confidentiality>18 <informationStatus>real</informationStatus>19 <urgency>urgent</urgency>20 </headerInformation>21 <situationRecord xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="AbnormalTraffic" id="TTI-71553ccb-728e-4ee3-9717-4afd308ce0f3-TTL25838637712020000-1">22 <situationRecordCreationTime>2023-10-10T12:44:13Z</situationRecordCreationTime>23 <situationRecordVersion>7</situationRecordVersion>24 <situationRecordVersionTime>2023-10-10T12:44:30Z</situationRecordVersionTime>25 <situationRecordFirstSupplierVersionTime>2023-10-10T12:44:30Z</situationRecordFirstSupplierVersionTime>26 <probabilityOfOccurrence>certain</probabilityOfOccurrence>27 <validity>28 <validityStatus>definedByValidityTimeSpec</validityStatus>29 <validityTimeSpecification>30 <overallStartTime>2023-10-10T12:44:13Z</overallStartTime>31 </validityTimeSpecification>32 </validity>33 <impact>34 <delays>35 <delayTimeValue>131.0</delayTimeValue>36 </delays>37 </impact>38 <groupOfLocations>39 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="Linear">40 <locationExtension>41 <openlr>42 <binary version="3">C81gjx4aeyOABwEMAWEjEw==</binary>43 </openlr>44 </locationExtension>45 </locationContainedInGroup>46 </groupOfLocations>47 <situationRecordExtension>48 <alertCEventCode>108</alertCEventCode>49 </situationRecordExtension>50 <abnormalTrafficType>queueingTraffic</abnormalTrafficType>51 <abnormalTrafficExtension>52 <averageSpeed>9.1</averageSpeed>53 </abnormalTrafficExtension>54 </situationRecord>55 </situation>5657[...]5859 </payloadPublication>60</d2LogicalModel>
Response – DATEX II payload specification (analysis of the received output)
The payload in the output is formatted as DATEX II, which is a European standard for the exchange of Traffic and Travel Information. TomTom supports version 1. Recommended documents are:
- DATEX II v1.0 User Guide version 1.0 ( DATEXIIv1.0-UserGuide_v1.0.pdf )
- DATEX II v1.0 Software Developers Guide version 1.0 ( DATEXIIv1.0-DevGuide_v1.0.pdf )
- DATEX II v1.0 Exchange Platform Specific Model version 1.0 ( DATEXIIv1.0-ExchangePSM_v1.0.pdf )
- A browsable DATEX II version 1.0 data dictionary ( DATEXIIv1.0-DataDictionnary_v1.0.zip )
The Elaborated Data Publication, used by TomTom, is described in more detail in section 4.11 of the DATEX II User Guide version 1.0.
Important: XSD schema
TomTom extended the data model with additional fields; the full XSD schema including extensions can be downloaded by clicking this Level B extension. It is a "Level B" extension of the standard XML schema: DATEXIISchema_1_0_1_0.xsd. Such an extension is interoperable with the "Level A" data model (see section 2.2.3 in the DATEX II User Guide version 1.0 for more information).
How the data is organized
Situation publication
The traffic information is provided as a SituationPublication. A SituationPublication is the
snapshot of the latest traffic data. A SituationPublication can contain several different
situations.
The service does not support a delta mechanism. Therefore, incremental updates are not possible.
Situation
A situation represents a traffic or travel incident comprising one or more traffic or travel
circumstances. These are linked by one or more causal relationships and apply to related locations.
Each traffic or travel circumstance is represented by a SituationRecord.
Situation record
A SituationRecord is one element of a situation. It is characterized by values at a given time,
defining one version of this element. When these values change, a new version is created. One
SituationRecord can be:
- a road or traffic related event (traffic element)
- an operator action
- a piece of information that is based on a non-road event
and can contain:
- an advisory
- details that impact the estimated time of arrival
Unique identifier
Each Situation has a unique identifier. Additionally, every SituationRecord also has a unique
identifier. This identifier is established when the Situation or SituationRecord is first created
in the DATEX II system database. As long as the situation exists, this identifier will always be
present within the system. The unique identifier has a fixed prefix "TT", followed by a string. No
further assumptions should be made about the identifier.
The identifier is unique across all supported countries.
Impact
If the current delay is available for a SituationRecord, the delayTimeValue is provided in the
Impact. If there is information about closed lanes, because of an accident or other incident, it can
be populated in ImpactDetails.
Related situation records
In some cases, there are multiple SituationRecords that are related to each other. For instance,
there can be a traffic jam that is caused by an accident. If the locations of these
SituationRecords overlap or are connected AND they occur in the same direction, then the
SituationRecords are contained in the same Situation. In that case, a single Situation contains
more than one SituationRecord.
Sometimes, it is possible that two SituationRecords are related to each other, but do not overlap.
For instance, one SituationRecord contains a diversion advice, located at a highway intersection.
Since the road is blocked farther along the segment, that is described in a different
SituationRecord. In that case, the SituationPublication does not contain a reference from one
SituationRecord to the other.
For the first example, consider combining the information from the SituationRecords in your end
application to let the end-user know there is a delay due to an accident. In the second example,
there is a diversion due to a road closure.
Default enabled information
The DATEX II data model has been extended to allow additional parameters. Some of these extensions are needed for the standard feed information and are explained in the following sections.
Validity period
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Specifies the validity of a
The Incident end time and Future incidents are optional features and not part of the standard information. |
1<situationRecord [...]>2 [...]3 <validity>4 <validityStatus>active</validityStatus>5 <validityTimeSpecification>6 <overallStartTime>2022-10-10T08:00:00Z</overallStartTime>7 </validityTimeSpecification>8 </validity>9 [...]10</situationRecord>
Location referencing
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Every OpenLR (see http://www.openlr.org) is a dynamic location referencing method that allows referencing of any road on the complete digital map. Because of its flexibility, it is possible to describe traffic events on high-level and lower-level road classes. The method is available free of charge. The Service uses binary format version 3, as described in the OpenLR whitepaper. The whitepaper, software developer kit, and open source reference implementations are available for download from the OpenLR website. TomTom offers support for third parties to implement and test their own implementations. |
1<groupOfLocations>2 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="Linear">3 <locationExtension>4 <openlr>5 <binary version="3">CwkmCSJZIRtmJQiDBE4bEg==</binary>6 </openlr>7 </locationExtension>8 </locationContainedInGroup>9</groupOfLocations>
See the section, Identifier-based location referencing using OSM way IDs for a location referencing specific for OSM maps or Identifier-based location referencing using GERS IDs for a location referencing specific for the Orbis map.
Average speed for jams
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | The average speed for congestion events, in km/h. |
1<situationRecord xsi:type="AbnormalTraffic" [...]>2 [...]3 <abnormalTrafficExtension>4 <averageSpeed>18.0</averageSpeed>5 </abnormalTrafficExtension>6</situationRecord>
Delay for jams
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | The |
1<situationRecord xsi:type="AbnormalTraffic" [...]>2 [...]3 <impact>4 <delays>5 <delayTimeValue>64.0</delayTimeValue>6 </delays>7 </impact>8 [...]9</situationRecord>
Alert-C event codes
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | The Alert-C event code describing the |
1<situationRecord [...]>2 [...]3 <situationRecordExtension>4 <alertCEventCode>115</alertCEventCode>5 </situationRecordExtension>6</situationRecord>
Refer to ISO TS 14819-2 at https://www.iso.org for Alert-C codes and conventions.
Language-specific texts
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | A |
1<situationRecord [...]>2 [...]3 <generalPublicComment>4 <comment>5 <value lang="en">The pass is free in both directions.</value>6 <comment>7 </generalPublicComment>8</situationRecord>
Probability of occurrence
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | The semantics of this field are deprecated and will be removed in the future. Do not use. The reason why this attribute is used at all is that in DATEX II v1.0 it is a mandatory field. |
1<situationRecord [...]>2 [...]3 <probabilityOfOccurrence>probable</probabilityOfOccurrence>4 [...]5</situationRecord>
Optionally activatable features
The DATEX II data model has been extended to allow additional parameters. The Service has the following possible extensions.
Identifier-based location referencing using OSM way IDs
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Identifier-based location referencing OSM way IDs (hereafter called 'IDLR-OSM') is offered as an alternative method of location referencing besides OpenLR. The IDLR-OSM is identified by the value The ID list can contain a list of OSM way IDs in the format
|
The following example shows a locationExtension element with an IDLR-OSM in the idlr element
indicated by the attribute method="OSM" that is composed of three OSM way IDs.
All IDs use the forward direction, the first ID uses a start-offset of 300 meters,
the second doesn't have offsets, and the third uses an end-offset of 203 meters. Since the end-offset is the
second offset in the list of offsets, it always requires an explicit mention of the start-offset
with 0 meters if the ID does not use a start-offset. The affected location is the concatenation of all IDs
minus the offset information.
1<situation [...]>2 <situationRecord [...]>3 [...]4 <groupOfLocations>5 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="Linear">6 <locationExtension>7 <openlr>8 <binary version="3">[...]</binary>9 </openlr>10 <idlr method="OSM">"F491249694#300 F568042661 F116413004#0#203"</idlr>11 </locationExtension>12 </locationContainedInGroup>13 </groupOfLocations>14 [...]15 </situationRecord>16</situation>
Identifier-based location referencing using GERS IDs
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Identifier-based location referencing Global Entity Reference System (hereafter called 'IDLR-GERS') is offered as an alternative method of location referencing besides OpenLR and IDLR-OSM. The IDLR-GERS is identified by the value The ID list can contain a list of GERS IDs in the format
|
The following example shows a locationExtension element with an IDLR-GERS in the idlr element
indicated by the attribute method="GERS" that is composed of two GERS IDs.
Both IDs use the forward direction, the first ID uses a start-offset of 561 meters, and the second uses an end-offset.
Since the end-offset is the second offset in the list of offsets, it always requires an explicit mention of the start-offset
with 0 meters if the ID does not use a start-offset. The affected location is the concatenation of all IDs
minus the offset information.
1<situation [...]>2 <situationRecord [...]>3 [...]4 <groupOfLocations>5 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="Linear">6 <locationExtension>7 <openlr>8 <binary version="3">[...]</binary>9 </openlr>10 <idlr method="GERS">F0871f428-80ff-ffff-047d-7fb9bb3ed230#561 F0881f428-80bf-ffff-047f-c80b78407632#0#298</idlr>11 </locationExtension>12 </locationContainedInGroup>13 </groupOfLocations>14 [...]15 </situationRecord>16</situation>
For more information on how to use GERS IDs, please visit the Overture Maps website.
Incident end time
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | This option predicts the expected ending time for the traffic incident such as the expected end time of a jam or a closure. This field is expressed as a UTC time (e.g., 14:22 UTC). These end times may be created by TomTom or originate from local road authorities (for journalistic events). |
1<situationRecord [...]>2 [...]3 <validity>4 <validityStatus>definedByValidityTimeSpec</validityStatus>5 <validityTimeSpecification>6 <overallStartTime>2023-10-10T08:00:00Z</overallStartTime>7 <overallEndTime>2023-11-13T00:00:00Z</overallEndTime>8 </validityTimeSpecification>9 </validity>10 [...]11</situationRecord>
Jam tendency
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | This feature indicates whether a jam is improving,
remaining stable, or becoming worse. The feature is
supported for the situation record type
|
1<situationRecord [...] xsi:type="AbnormalTraffic" [...]>2 [...]3 <trafficTrendType>trafficBuildingUp</trafficTrendType>4 [...]5</situationRecord>
Weather-related messages
Important
This feature is now offered as part of the TomTom Hazard Warnings product.
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | This feature reports messages for road segments that could be impacted by severe weather. Snow or heavy rain conditions use suitable Alert-C event codes and DATEX II classifications. The following Alert-C event codes and weather conditions are used:
|
Jam ahead warnings
Important
This feature is now offered as part of the TomTom Hazard Warnings product.
| Fields |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Selecting this option generates special warning messages when a location registers high-speed differences. Specifically, when the tail end of the jam is projected to intercept oncoming traffic, creating a potentially dangerous situation. The user can enable messages for only jam-ahead warnings or have them delivered next to all regular messages. An OpenLR point along line reference is used for
this message. The jam ahead warning is recognized by
a |
1<situationRecord [...] xsi:type="AbnormalTraffic" [...]>2 [...]3 <groupOfLocations>4 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="Point">5 <locationExtension>6 <openlr>7 <binary version="3">KwchAiYFHQEfGf8LBSABUEc=</binary>8 </openlr>9 </locationExtension>10 </locationContainedInGroup>11 </groupOfLocations>12 [...]13 <abnormalTrafficExtension>14 <averageSpeed>29.0</averageSpeed>15 </abnormalTrafficExtension>16</situationRecord>
Average speed for journalistic events
| Fields |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Selecting this option adds the average speed values for journalistic messages (for example, road works, or lane restrictions). This is the average speed as measured by TomTom. We created DATEX II extensions for each journalistic
event type that supports speeds (also see Fields
above). In addition to the speed information the delay
is indicated as part of the |
1<situationRecord [...] xsi:type="GeneralObstruction" [...]>2 [...]3 <impact>4 <delays>5 <delayTimeValue>34.0</delayTimeValue>6 </delays>7 </impact>8 [...]9 <generalObstructionExtension>10 <averageSpeed>59.6</averageSpeed>11 </generalObstructionExtension>12</situationRecord>
All other extension types listed under Field work the same way as GeneralObstruction.
Turn-dependent jams
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Selecting this option provides the user with turn-dependent jams information. The user receives messages when a portion of the jam is projected to affect travel only if following in the direction of the jam. Common use cases include: congestion on exit ramps, entry ramps, turn-lanes, and so on. To find the actual affected location, the (conditional) offset must be applied from the end of the location. 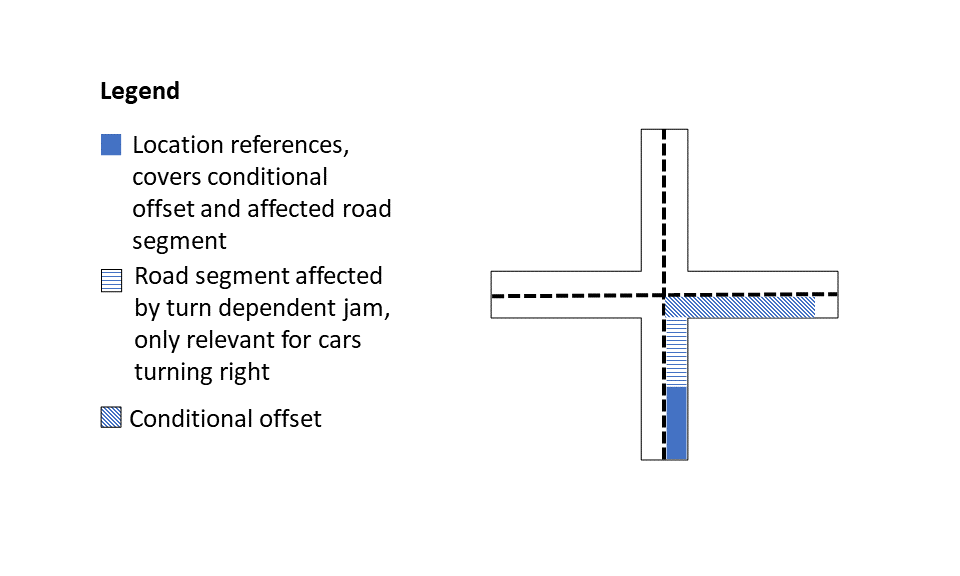 |
1<situationRecord [...]>2[...]3<situationRecordExtension>4 <alertCEventCode>115</alertCEventCode>5 <conditionalOffset>151</conditionalOffset>6</situationRecordExtension>7[...]8</situationRecord>
HOV jams
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Selecting this option provides the user with high-occupancy vehicle
(HOV) jams information. This feature is only available in combination
with the location referencing method OpenLR.
The |
1<situationRecord [...]>2 [...]3 <groupOfLocations>4 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="Linear">5 <locationExtension>6 <openlr>7 <binary version="3">KwSSoyRHmAEVCP18/zsBRds=</binary>8 </openlr>9 </locationExtension>10 <supplementaryPositionalDescription>11 <lanes>carPoolLane</lanes>12 </supplementaryPositionalDescription>13 </locationContainedInGroup>14 </groupOfLocations>15 [...]16</situationRecord>
Incident node name
| Fields |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Selecting this option provides node names for cross-streets at the beginning and end of the road segment. |
1<situationRecord [...]>2 [...]3 <groupOfLocations>4 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="Linear">5 <locationExtension>6 [...]7 <fromNodeName>8 <name>Globe St/S Main St (Broadway St/MA-138)</name>9 </fromNodeName>10 <toNodeName>11 <name>I-195 (Broadway St/MA-138)</name>12 </toNodeName>13 [...]14 </locationExtension>15 </locationContainedInGroup>16 </groupOfLocations>17 [...]18</situationRecord>
Road number
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Selecting this option provides the road identifier or road number of the affected location. |
1<situationRecord [...]>2 [...]3 <groupOfLocations>4 <locationContainedInGroup xsi:type="Linear">5 <locationExtension>6 [...]7 <roadNumber>A3</roadNumber>8 </locationExtension>9 </locationContainedInGroup>10 </groupOfLocations>11 [...]12</situationRecord>
Future incidents
| Fields |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Selecting this option includes incidents whose start time is in the
future (for example, planned roadworks, or road closures).
The field is expressed as a UTC time (e.g., 14:22 UTC).
The start time of future incidents is after the publication time.
The |
1<?xml version="1.0" ?>2<d2LogicalModel3 xmlns="http://datex2.eu/schema/1_0/1_0"4 modelBaseVersion="1.0">5 [...]6 <payloadPublication7 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"8 xsi:type="SituationPublication" lang="en">9 <!-- time when snapshot was created -->10 <publicationTime>2023-10-10T00:00:00Z</publicationTime>11 <situation [...]>12 <situationRecord [...]>13 [...]14 <validity>15 <validityStatus>suspended</validityStatus>16 <validityTimeSpecification>17 <!-- start time of the incident -->18 <overallStartTime>2023-10-15T00:00:00Z</overallStartTime>19 </validityTimeSpecification>20 </validity>21 [...]22 </situationRecord>23 </situation>24 </payloadPublication>25<d2LogicalModel/>
Map version
| Field |
|
|---|---|
| Description | This option provides the names and versions of the maps that were used to create the content. |
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>2<d2LogicalModel xmlns="http://datex2.eu/schema/1_0/1_0" modelBaseVersion="1.0">3 [...]4 <payloadPublication5 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"6 xsi:type="SituationPublication" lang="en">7 [...]8 <payloadPublicationExtension>9 <mapVersion>nam2023.06.060</mapVersion>10 </payloadPublicationExtension>11 <!-- list of situation elements follows -->12 [...]13 </payloadPublication>14</d2LogicalModel>