EV Routing
Introduction
The Navigation System provides a suite of Electric Vehicle (EV)-specific features to enhance the driving and charging experience. Key capabilities include:
- Long Distance EV Routing (LDEVR): Automatic planning of charging stops along a route
- Searching for nearby charging stations
- Displaying estimated driving range on the map
This document is for integrators of TomTom's Automotive Navigation Application, Navigation SDK, and the Online Routing API into cars and apps. It provides:
- An overview of LDEVR features
- Key assumptions and limitations
- Data formats, request and response structures
- Integration guides for connecting LDEVR with the vehicle's Battery Management System (BMS)
For product-specific details, see the documentation for the Automotive Navigation Application, Navigation SDK, and the Online Routing API.
Long Distance EV Routing overview
LDEVR automatically suggests charging stops when a route exceeds the vehicle's range. It generates an optimized route with charging stops based on the vehicle's battery level, charging capabilities, and consumption characteristics.
LDEVR provides a charging plan before the trip and updates it during driving, delivering accurate estimates for travel time and time of arrival.
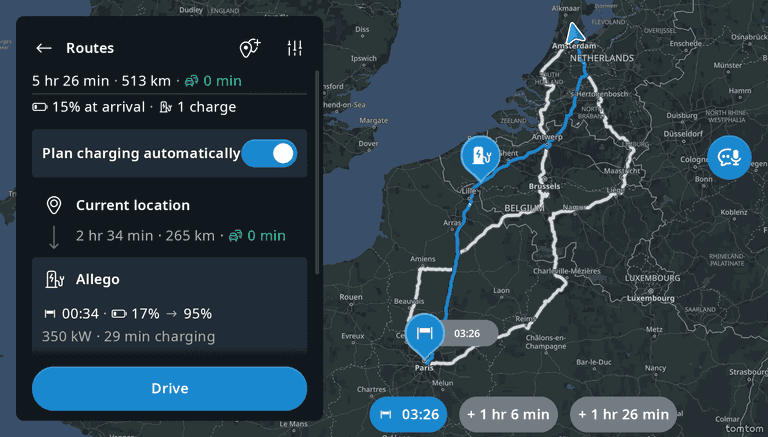
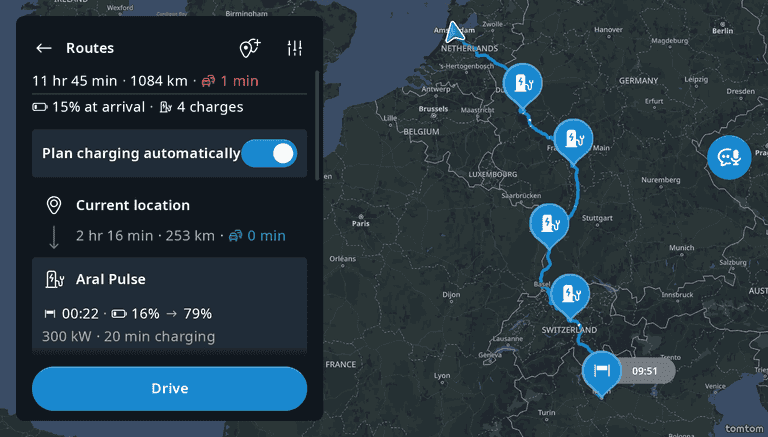
Estimated Travel Time (ETT) and Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA)
By planning charging stops instead of ad-hoc charging, the vehicle can automatically pre-condition the battery for Direct Current (DC) fast charging. Drivers see information about upcoming stops in the Navigation System, including suggested charging times and State of Charge (SoC) changes (from X% to Y%) based on charging station and vehicle capabilities. For more information, refer to Consumption Model Integration | Nominal battery capacity.
Fully automatic vs. manual EV route planning
Users can enable or disable LDEVR through the UI setting "Plan charging automatically" (default: on). When active, charging stops are suggested at the planning stage for out-of-range destinations and when the battery SoC is insufficient to reach the destination within the minimum SoC buffer. See Preferences and Personalization | Recommended default SoC values. Drivers can change suggested charging stops or add different stops using the Search functionality. The route adjusts automatically to consider the new location.
TomTom's consumption model determines whether a destination is within range by using vehicle parameters and signals to calculate driving distance based on map attributes.
EV Routing system context and data flow
The accuracy and effectiveness of EV navigation features rely on the integration between the Navigation System and the vehicle's Battery Management System (BMS). Integration can range from simple (BMS provides SoC, charging curve, consumption curve, and supported charging connectors) to advanced (battery conditioning energy consumption, driving condition-dependent consumption curves, and temperature-dependent consumption curves). The diagram below provides a simplified representation of the various systems involved in LDEVR. The EV Battery Management System The diagram below shows the systems involved in LDEVR. The EV Battery Management System provides all necessary battery information, enabling the Navigation System (composed of Navigation Application, Navigation SDK, and Online Routing API) to perform LDEVR. This includes state of charge, maximum battery capacity, charging curves, and more. This information is typically provided via the In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI) system and used by the Navigation System, or obtained via the OEM Connected Car Cloud and used by a Companion App.
The OEM Connected Car Cloud provides vehicle data or functions to systems outside the vehicle context. The name varies across OEMs.
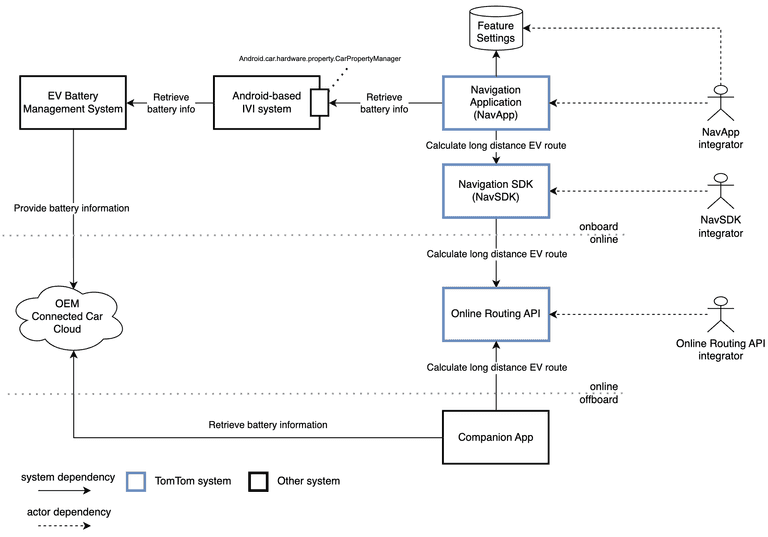
The Navigation System or Companion App requests the Online Routing API to calculate an LDEV route. The necessary battery information is retrieved from the IVI system or OEM Connected Car Cloud.
If the retrieved battery information format does not match the required input formats for LDEVR, conversion to required units or data types may be necessary.
The required inputs can be supplied through various APIs, depending on the integrator role. The semantics remain unchanged. The APIs are explained in API requirements.
Integration details
- Consumption model integration – Learn about the essential parameters needed to accurately predict energy consumption along the route, estimate state of charge upon arrival, and display range on the map.
- Charging parameters – Understand the parameters required to estimate time spent at charging stations, including charging curves and connector types.
- Preferences and personalization – Explore the configurable values and settings that allow you to customize the LDEVR experience for different use cases and vehicle types.
- Vehicle integration – Learn how to integrate your vehicle with the Navigation System to enable LDEVR features.
- API requirements – Understand how to map vehicle and configuration parameters to the Navigation System APIs for your specific product.