UI components
The TomTom SDKs provide UI elements to use with search in your application. To use them, add the SearchUI module to your application. SearchUI works with fuzzy search.
If you haven’t set up the project with the TomTom SDKs yet, read how to do it in the Project setup guide.
implementation("com.tomtom.sdk.search:ui:1.1.0")
The SearchUI module contains:
- SearchView: Input bar for the search phrase.
- SearchResultsView: View to attractively display search results.
- SearchSuggestionView:
SearchSuggestionview. - SearchFragment: Single fragment to bring SearchView, SearchResultsView and SearchSuggestionView functionality together.
Search view
The TomTom SDKs provide a predefined element for inserting a search query. It contains EditText to allow the user to enter text and a Clear Button for clearing entered text.

- Add
SearchViewin your XML layout. CAUTION: Make sure you’re usingSearchViewfrom the TomTom SDKs rather than the Android one.1<com.tomtom.sdk.search.ui.SearchView2 android:id="@+id/search_view"3 android:layout_width="match_parent"4 android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> - Get the instance of the
SearchViewin your Activity/Fragment class.private val searchView: SearchView by lazy { findViewById(R.id.search_view) } - Set the
SearchViewListenerto report on interactions withSearchView.SearchViewListenerhas 3 methods that are triggered when specific actions occur:onSearchQueryCancel(): Called when the user taps the cancel button.onSearchQueryChanged(String): Called whenever the query changes.onCommandInsert(String): Reacts when the entered text is one of the commands provided inSearchProperties.
1searchView.searchViewListener = object : SearchViewListener {2 override fun onSearchQueryCancel() {3 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */4 }56 override fun onSearchQueryChanged(input: String) {7 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */8 }910 override fun onCommandInsert(command: String) {11 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */12 }13}
A query can also be set programmatically by calling SearchView.setQuery(String), which sets the text in the SearchView and triggers a search. In the same way, you can also clear the input using the SearchView.clear() method. The SearchView.hasInput() method checks if the search bar is not empty.
1searchView.setQuery("Amsterdam")2searchView.clear()3val isNotEmpty = searchView.hasInput()
Search results view
Once you have search results, the TomTom SDKs can help you show them to the user. Use SearchResultsView to present search results attractively. If an error occurred during the search request, SearchResultsView can also display that in a user-friendly way.
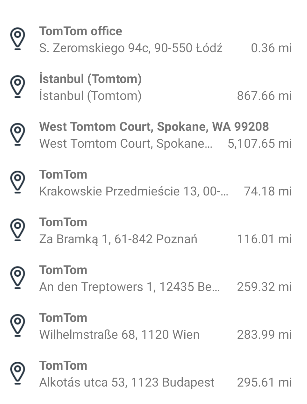
The first step is to add the SearchResultsView to your XML layout file.
1<com.tomtom.sdk.search.ui.SearchResultsView2 android:id="@+id/search_results_view"3 android:layout_width="wrap_content"4 android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
Then get the instance of SearchResultsView in your Activity/Fragment class. Now SearchResultsView is ready to use.
To display search results, use the SearchResultsView.update(List<Place>, String) method with the list of Place objects returned from the search and optional query to highlight matching result. Calling SearchResultsView.update(List<Place>) only with the first argument disables highlighting. You can also use other searches (see Autocomplete and Fuzzy Search) and create a list of Place objects from their results.
searchResultsView.update(results, query)
Call SearchResults.displayError(String) to display an error message.
If you are using SearchView, you can call it with the SearchViewListener.onSearchError(Throwable) method.
searchResultsView.displayError(error.message!!)
Once the list of results is displayed, the user may want to select one for more information. Use SearchResultClickListener to be notified when the user taps on a search result. It provides the Place object of the result that the user selected.
1searchResultsView.searchResultClickListener = SearchResultClickListener { placeDetails: PlaceDetails ->2 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */3}
You can also clear all the results from the SearchResultsView in the code.
searchResultsView.clear()
Search suggestion view
TomTom’s Search Suggestion query can be used to create autocomplete functionality for the user. SearchSuggestionView suggests what the user may be searching for by processing their partial input. If the suggestion is correct, the user can tap on it to perform the search.
It wraps the query in an attractive container.

First add SearchSuggestionView to your XML layout.
1<com.tomtom.sdk.search.ui.SearchSuggestionView2 android:id="@+id/search_suggestion_view"3 android:layout_width="wrap_content"4 android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
Then get the instance of the SearchSuggestionView in the Activity/Fragment class. Add the required parameters and set the SearchSuggestion to be displayed.
1searchSuggestionView.setSuggestion(2 SearchSuggestion(3 title = "TomTom",4 subtitle = "Amsterdam",5 query = "TomTom Amsterdam",6 imageResId = R.drawable.ic_office7 )8)
The last step is to detect a user tap. To do so, set the SearchSuggestionClickListener. The listener provides the SearchSuggestion that was set to the SearchSuggestionView.
1searchSuggestionView.listener =2 SearchSuggestionClickListener { suggestion: SearchSuggestion? ->3 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */4 }
Search fragment
The search fragment combines all of the views described above into a single fragment and adds search capabilities. If the search returns results, the SuggestionSearchView is hidden.
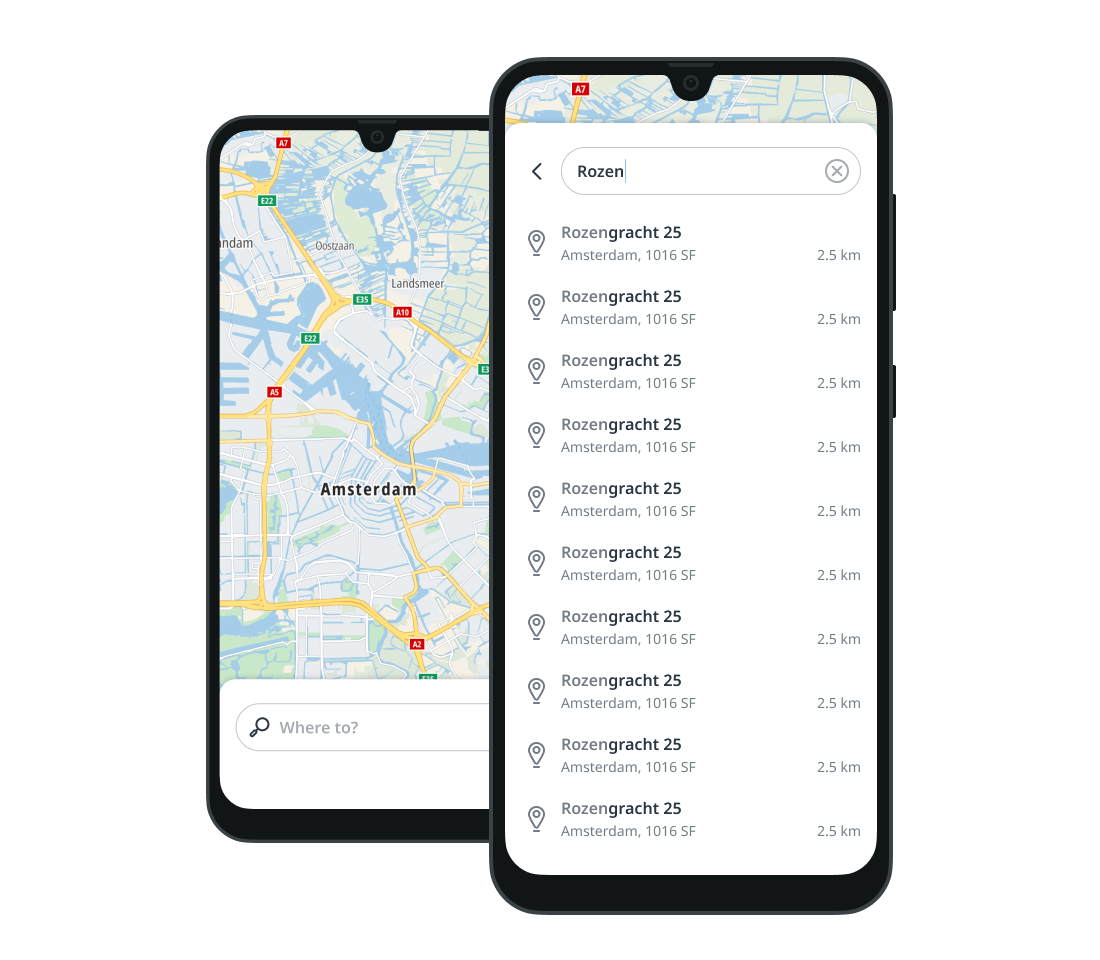
Start by adding the container for the SearchFragment to your layout file.
1<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView2 android:id="@+id/search_fragment_container"3 android:layout_width="match_parent"4 android:layout_height="match_parent" />
Create a new instance of the SearchFragment. The SearchFragment.setSearchApi(SearchApi) method has to be called for it to be usable (preferably as part of onViewCreated() Android framework callback handler).
To do so you will need a SearchProperties object. The only required parameter is a TomTom API key that is valid for the Search API. See this link for how to get a TomTom API key.
You can configure the search by setting optional SearchApiProperties. The last parameter is the list of user commands that SearchView will recognize. When the user enters one of the commands listed, the SearchViewListener.onCommandInsert(String) method is triggered with the command as the parameter.
1val searchApiParameters = SearchApiParameters(2 limit = 5,3 position = GeoPoint(52.377956, 4.897070)4)5val searchProperties = SearchProperties(6 searchApiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY",7 searchApiParameters = searchApiParameters,8 commands = listOf("TomTom")9)
Then attach the new fragment to its parent using FragmentManager.
1val searchFragment = SearchFragment.newInstance(searchProperties)2supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction()3 .replace(R.id.search_fragment_container, searchFragment)4 .commitNow()
SearchFragment is a user interface wrapper for Search. This means you have to set Search to the fragment.
searchFragment.setSearchApi(search)
By default, SearchFragment performs a search for the entered query in SearchView and displays the results in SearchResultsView.
To listen for events that occur during the process, set the SearchFragmentListener. This triggers the appropriate methods as in the separate views described above.
1val searchFragmentListener = object : SearchFragmentListener {2 override fun onSearchBackButtonClick() {3 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */4 }56 override fun onSearchResultClick(placeDetails: PlaceDetails) {7 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */8 }910 override fun onSearchError(throwable: Throwable) {11 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */12 }1314 override fun onSearchQueryChanged(input: String) {15 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */16 }1718 override fun onCommandInsert(command: String) {19 /* YOUR CODE GOES HERE */20 }21}22searchFragment.setFragmentListener(searchFragmentListener)
Note that SearchFragment also adds a back arrow button. The SearchFragmentListener.onSearchBackButtonClick() method is triggered when the user taps on it. It can be removed.
searchFragment.enableSearchBackButton(false)
Next steps
Since you have learned how to use the search UI elements, here are recommendations for the next steps: