Introduction
What’s new?
- Richer online mapping with TomTom Orbis map
- Easier integration through initialization surface
TomTomSdk.initialize(…)that handles all of the configuration needed to begin working on your application. This now includes both Maps and Navigation SDK. - TomTom example app using Jetpack Compose for you to use and start building fast.
- We have removed the Maps SDK, and we now use only the TomTom Maps and Navigation SDK.
For more details check the release notes and the migration guide.
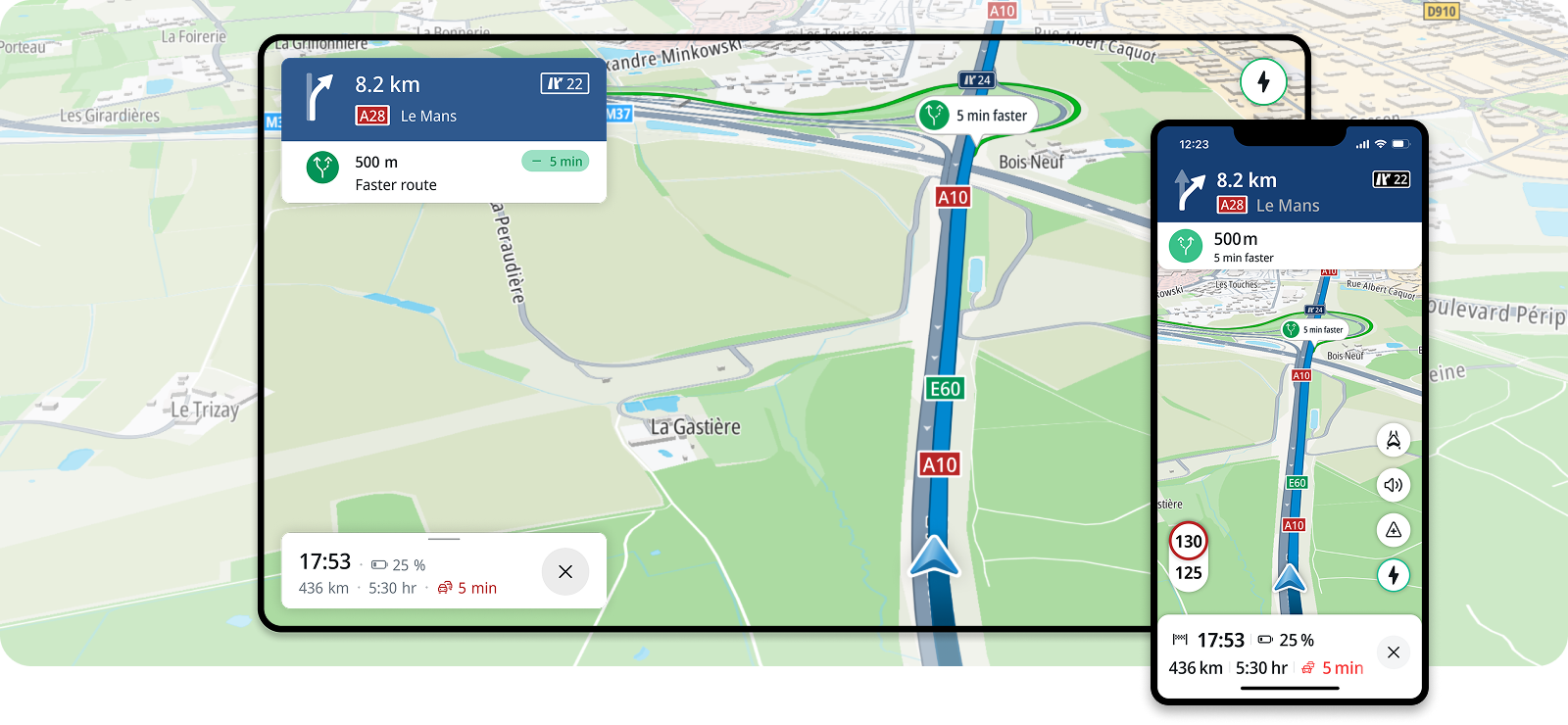
The Maps and Navigation SDK, powered by TomTom Orbis map, equips developers with extensive online mapping capabilities and enables seamless integration of advanced navigation features into Android applications. With this powerful SDK, you can quickly implement essential functionalities such as map visualization, location, search, routing, and driver guidance.
Whether you’re creating map-oriented scenarios or building a comprehensive navigation solution, the SDK simplifies the development process, allowing you to deliver high-quality applications more efficiently. For an easier start, you can leverage TomTom example app that illustrates the main navigation use cases, helping you understand how to make the most of the SDK.
Key features
The Maps and Navigation SDK offers key features to help you every step of the way:
Map Display
Display and interact with maps using TomTom’s high-quality rendered maps.
Search
Add search functionality to your application, enable autocomplete results and allow driver to search along the route.
Turn by Turn
Provide visual and audio instructions along a route and handle various events like route deviations and destination arrivals.
Traffic
Enable traffic incidents on a route along with your guidance and detail the various incident types, like traffic jams, roadworks, and closed roads.
Online First
Create seamless navigation experience regardless of connectivity. Fallback to offline map for sustained connectivity loss. BETA *
EV Experience
EV experience. Delight EV drivers and reduce range and charging anxiety with TomTom EV — a future‑ready platform unifying planning, search, driving and charging. BETA *
* For more information about BETA APIs and guidance on their usage, please contact us
Code samples
TomTom provides an example app where you can explore practical implementations of the main navigation features, map features and use cases.
Get started with the example app